Scalp folliculitis has different manifestations and different forms of treatment. Therefore, it is essential to know and treat them.
Folliculitis is a chronic or acute inflammation of hair follicles, which are spread throughout all areas of the body that have hair. Normally uncomfortable, they tend to appear on the face, armpits, back, buttocks, groin and also on the scalp. In this sense, it is important to understand more about scalp folliculitis. In certain cases, it can lead to permanent hair loss, in this case, hair, as well as leaving eternal scars.
Scalp folliculitis can happen to anyone. It is normal for the problem to manifest itself more in situations of low immunity. Furthermore, it also affects overweight, black and Asian people in greater numbers. However, both men and women suffer from its occurrence, but the treatment possibilities are diverse: all that is needed, first of all, is a correct diagnosis in advance. Depending on its severity, treatment usually involves improved hygiene and antibiotics, both local and oral.
To better understand scalp folliculitis, check out everything you need to know about the problem below. Also learn about its different manifestations and ways to treat the situation.
What is folliculitis?
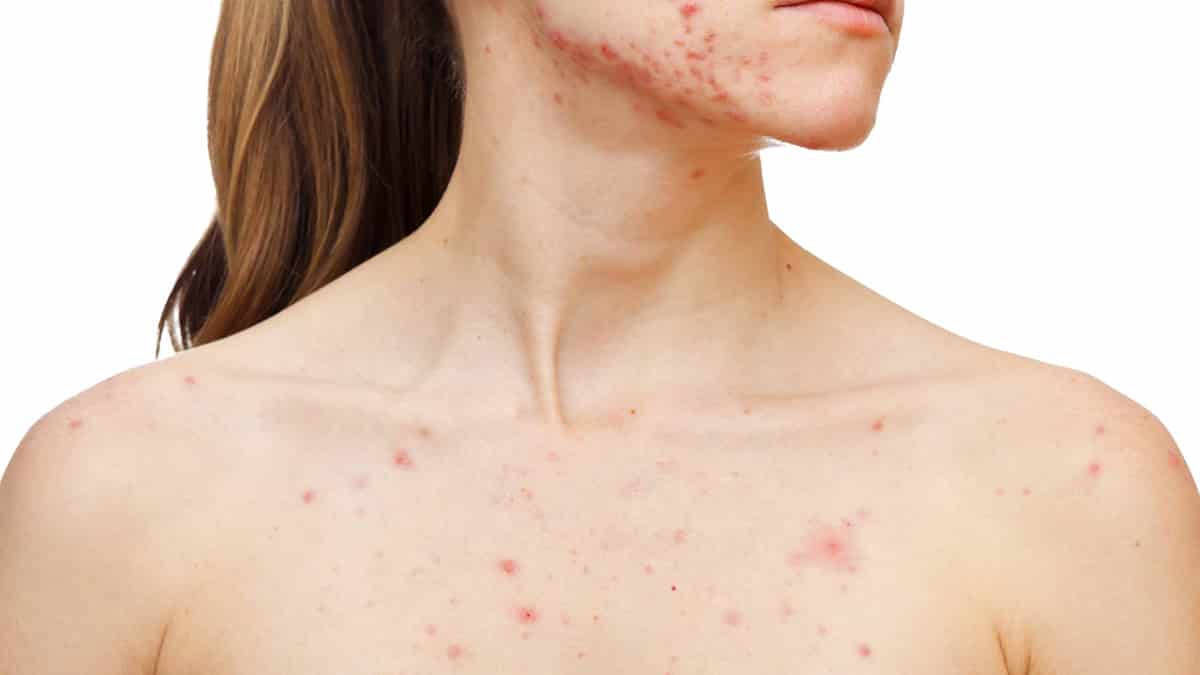
But after all, what is folliculitis? The occurrence is an inflammation of the region close to the hair follicle. This means that it can affect any region that has hair. When it occurs on the scalp, it is called hair folliculitis. Its causes are usually divided into infectious and inflammatory. In infectious cases, for example, the invasion of a microorganism into the hair follicle triggers an inflammatory reaction. The most common are:
- Viral
- Fungal
- Bacterial
The difference between inflammatory and infectious folliculitis is that, even though all infectious folliculitis has inflammation, not all inflammatory folliculitis has an infectious agent. There are also cases of the problem developing without contamination, based on low immunity, hair shape or other unknown causes.
What is hair folliculitis?

In this sense, hair folliculitis presents the same characteristics as a normal condition, but on the scalp. It does not go unnoticed, as it is marked by pimples, scabs and wounds. Additionally, you may still feel itchy, painful, have bleeding or pus. Some cases are accompanied by permanent baldness and hair loss, which worsens the discomfort.
Causes of scalp folliculitis
Even though there are many causes for the manifestation of folliculitis on the scalp, one of the main ones is infection with Staphylococcus aureus (staphylococci). However, many other fungi and bacteria can be the source of the problem. Since scalp follicles are denser, the more damage there is, the greater the chance of developing folliculitis. After all, the region will have low “immunity”. Other possibilities are:
- Excessive sweating
- Dermatitis
- Inflammatory conditions (wounds)
- Constant use of antibiotics
In the case of superficial folliculitis, its cause is usually related to a lack of hygiene, friction from the constant use of hats and caps and also excessive ointments and creams in the area. On the other hand, deep folliculitis is an intense infection in the hair follicles.
Infectious hair folliculitis
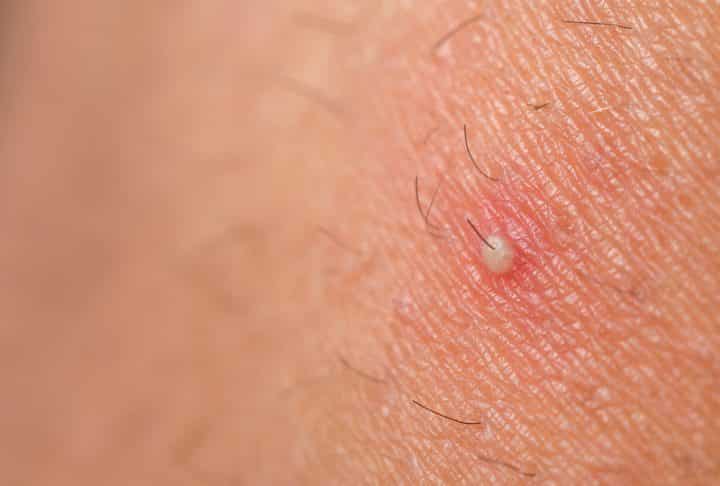
In this sense, scalp folliculitis occurs through contamination of the hair root, caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. In order to reach the hair follicle, the agent needs to cross the skin barrier. It is weakened after trauma to the skin close to the hair. Such traumas are usually habits, such as:
- passing your hand or scratching your scalp frequently;
- shave the head;
- hair prosthetics or mega hair;
- picking off scabs or balls that form on the head;
- trichotillomania, or the habit of pulling out hair;
- wear tight caps, caps and hats.
Therefore, when the skin is damaged, it becomes even easier for an agent to enter the region and infect the follicle. It is worth remembering that infections are contagious, that is, they can pass from one person to another. Therefore, it is essential to be careful about contact with others. Below, check out the main infections associated with folliculitis.
1 – By bacteria
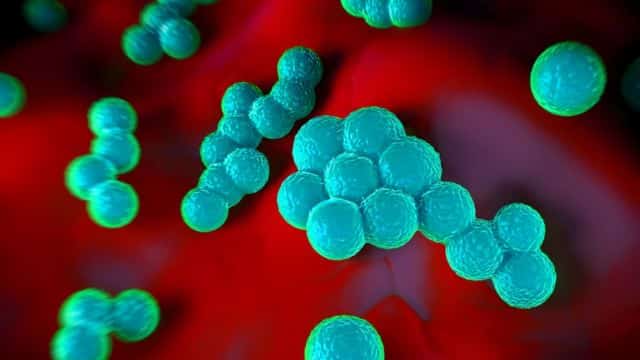
The most common scalp folliculitis is caused by infection with the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, or staphylococci. This bacteria is part of the microorganisms that live on the surface of the body and scalp skin. This way, when it’s outside, the bacteria don’t cause many problems. However, after skin damage, it is capable of causing infections with different clinical manifestations.
- Superficial folliculitis: the most common of all, it usually causes painful pimples to form on the scalp. Furthermore, depending on the number of injuries, they can cause painful bumps and lumps to appear on the ears and back of the neck.
- Deep hair folliculitis: when the bacteria is able to reach a deeper region of the follicle, it triggers, for example, sycosis. The condition is characterized by deep abscesses and nodules, red, swollen areas with pimples around the hair. Typically, the occurrence manifests itself in the beard, but it can also end up on the scalp.
- Boil: boils and carbuncles are also consequences of deep hair folliculitis. However, they also tend to affect the sebaceous gland. In the case of a boil, the lesion is well located around the thread. It precedes swelling, pain and redness. The center of the lesion even accumulates pus until it drains spontaneously.
- Carbuncle: in this case, the infection is even deeper than that of the boil. Occurring on the back of the neck, it is accompanied by painful swelling and fever.
2 – Fungal
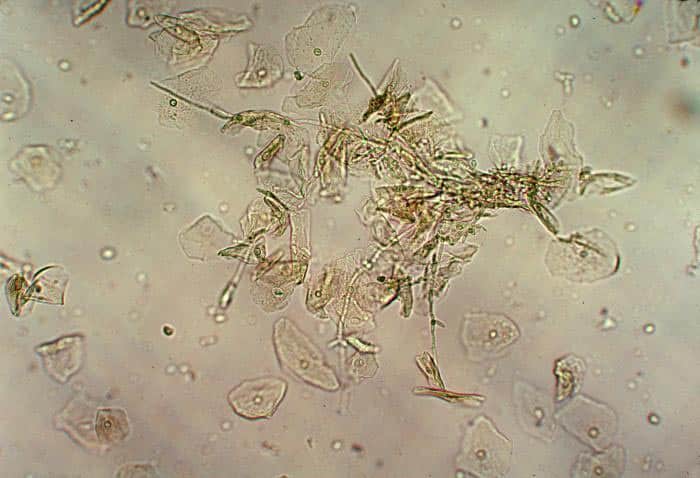
However, even if it is not that frequent, you can still end up with fungal contamination of the hair follicle. Fungi are part of the skin flora, but cause fewer infections and inflammation. Thus, when fungal folliculitis occurs, it is usually an isolated manifestation, or accompanied by ringworm. When accompanied by ringworm, folliculitis occurs due to fungi that already exist in the earth, coming from direct contact with already infected people or cats, dogs and horses.
Isolated fungal hair folliculitis is caused by yeasts such as Candida sp and Malassezia. People who are bedridden, have severe seborrheic dermatitis and are immunosuppressed are those most affected by the problem.
3 – Folliculitis decalvans
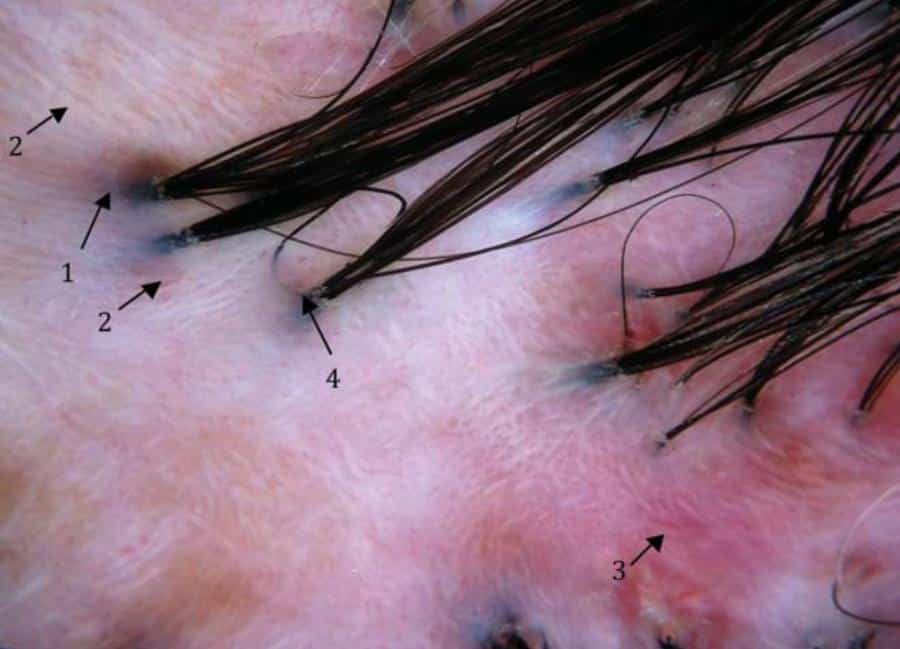
In this case, folliculitis is characterized by inflammation and destruction of the follicle, which is then replaced by a scar. Its cause remains unknown. Furthermore, as it is not an infectious condition, folliculitis decalvans is not contagious. Here, the bacteria is not the direct agent of the problem, but perhaps responsible for triggering an abnormal inflammatory response in the body.
Thus, destruction occurs, forming fibrosis and scarring of the skin around the hairs. The rest of the hairs come out in small tufts in a single follicular ostium, or hole. The situation is called polytrichia, or “doll strings”. The appearance of folliculitis decalvans presents itself as hardened and swollen red plaques, as well as clustered strands surrounded by pus. The problem is more common in adult and immunosuppressed men.
4 – Folliculitis on the dissecting scalp
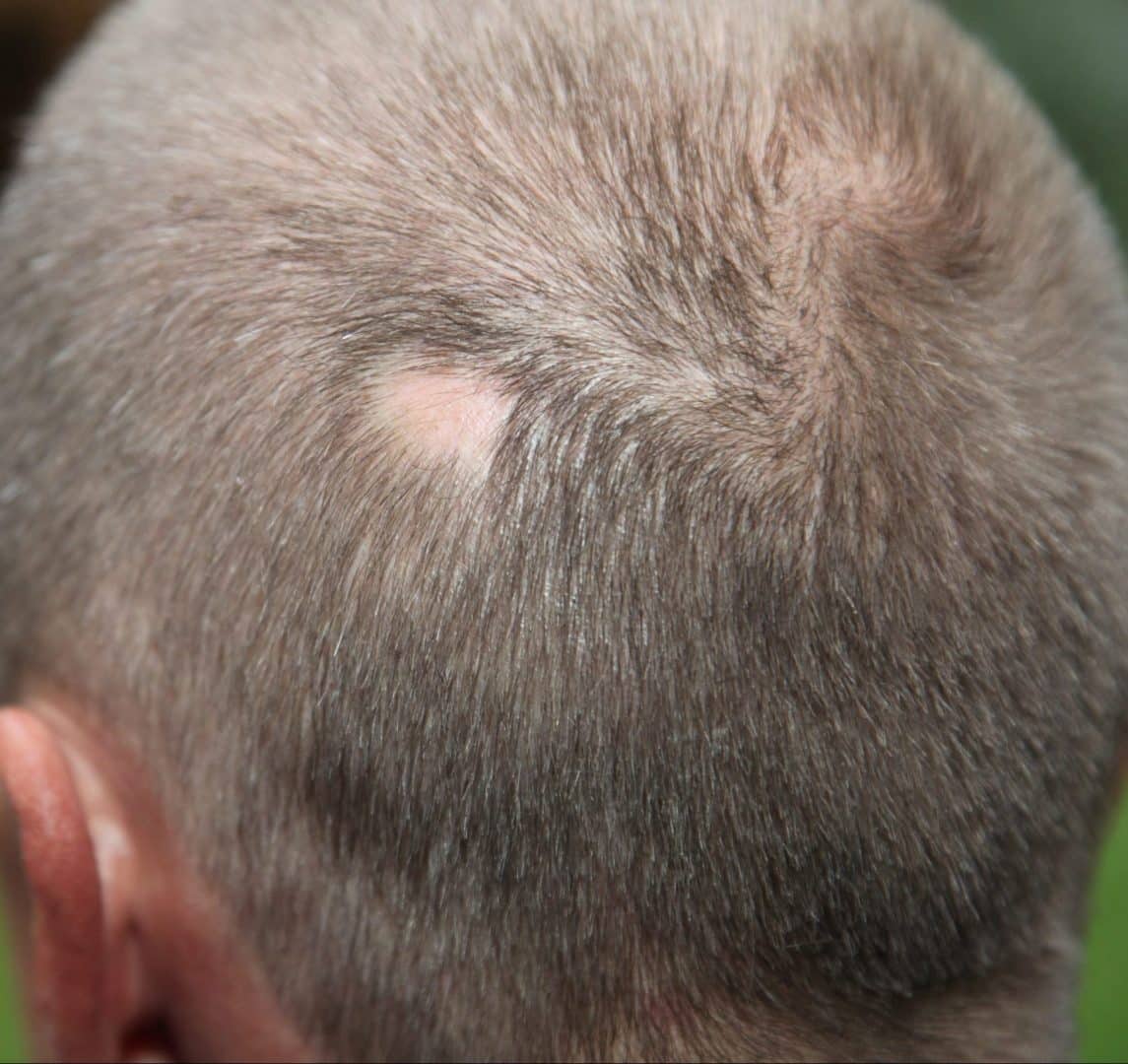
On the other hand, folliculitis dissecans, despite being inflammatory, is neither infectious nor contagious. Serious, folliculitis is part of a group of intense inflammatory reactions of the skin. These include hidradenitis and acne conglobata. There is also abscessant folliculitis, which is characterized by floating nodules and interconnected abscesses, with fistulas responsible for draining purulent secretions from the scalp. Normally, the inflammatory reaction is so intense that it leads to hair loss, as well as tissue fibrosis and permanent alopecia.
Thus, there are still other situations that can affect the scalp and cause hair folliculitis. Are they:
- Actinic folliculitis;
- Necrotic acne;
- Eosinophilic folliculitis;
- Planopilar lichen;
- Acneiform eruption;
- Folliculitis due to chemotherapy medication.
How to treat scalp folliculitis

First of all, it is essential to understand that early diagnosis and treatment are the best chance of controlling the situation as quickly as possible. This way, a worsening of the condition or new manifestations can be avoided. However, fundamental measures to remedy the situation tend to be to effectively improve immunity and block what causes folliculitis. This can be done by prescribing medication from a professional, such as antibiotics and topical or oral anti-inflammatories. Certain cases require more complex treatments.
In this sense, in cases such as folliculitis decalvans, treatment may even include ointments and infiltration with corticosteroids and medications with isotretinoin. Keloid folliculitis can even affect cases where surgery is necessary to remove the keloids that form. Cases like dissecting are a combination of all treatments: abscess drainage, antibiotics, isotretinoin, corticosteroids and surgery.
Prevention of scalp folliculitis
Finally, in order to avoid a situation of folliculitis on the scalp, extra measures can be taken to strengthen the region’s barrier and also immunity. Are they:
- Do not scratch or touch the lesions;
- Wash your hair daily, especially after sweating;
- Do not tie your hair tightly;
- Be careful when applying creams and oils close to the hair roots;
- Avoid sharing combs and brushes, towels and personal hygiene objects in general;
- Only enter pools and bathtubs that are sanitized;
- Use mild shampoos with an appropriate pH;
- Avoid shaving hair with machine 0 or 1.
So, what did you think of this article about scalp folliculitis? If you’re interested, also check out Folliculitis – What it is, what causes it and 8 habits to help you get rid of it
Sources: Clínica Doppio, Juro Valendo, Médico Respondes

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13




