Scalp folliculitis is the inflammation of hair follicles, causing symptoms such as red bumps or pimples on the hairline, intense itching, pain or sores with crusts or pus, or even hair loss.
This type of folliculitis can be caused by infections caused by bacteria, fungi, mites or viruses, or by autoimmune changes, and is more common in people who frequently wear wigs, caps, hats or helmets, for example.
Folliculitis treatment is carried out by a dermatologist and varies according to its cause, and generally involves the use of antibiotics, antifungals, retinoids, or even surgery.

Symptoms of scalp folliculitis
The main symptoms of scalp folliculitis are:
- Red polka dots;
- Pimples with a white tip;
- Intense itching or pain;
- Wounds due to scratching;
- Formation of wounds with crusts or pus, which can also bleed.
Furthermore, depending on the type of scalp folliculitis, hair loss may also occur, which in some cases may be permanent.
In the presence of symptoms of folliculitis on the scalp, it is important to consult a dermatologist to identify its cause and type, and thus begin the most appropriate treatment.
If you experience symptoms of scalp folliculitis, make an appointment with a dermatologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of scalp folliculitis is made by a dermatologist through the evaluation of symptoms, health history and physical examination observing the characteristics of the lesions on the scalp.
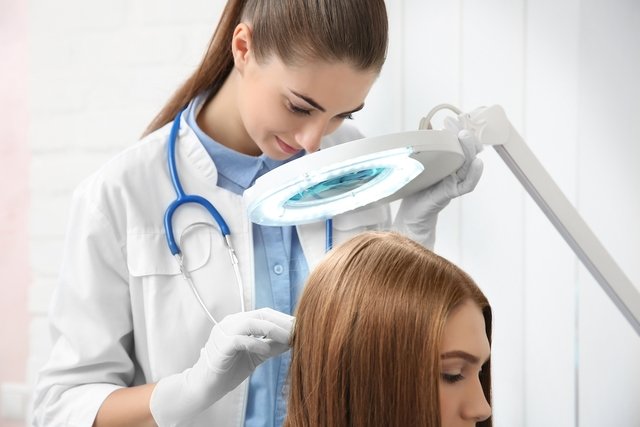
Generally, no additional examination is necessary, however, a KOH examination may be performed to confirm fungal infection, in addition to the Wood’s lamp examination. See how it is done and examine the Wood’s lamp.
In addition, a culture test may also be requested to identify the type of microorganism that is causing folliculitis on the scalp.
Possible causes
Scalp folliculitis is caused by infections by fungi, bacteria, mites or viruses, or by autoimmune changes, resulting in inflammation of the hair follicles, which is the structure in the skin where the hair roots are located.
Some factors can increase the risk of developing scalp folliculitis, such as:
- Frequent use of wigs, caps, hats or helmets;
- Shaving your hair or frequently scratching your scalp;
- Frequent use of “ponytails” or very tight braids;
- Weakened immune system;
- Use of hair products that can clog hair follicles;
- Use of antibiotics or topical corticosteroids for a long time;
- Immersion in bathtubs or swimming pools that are not properly sanitized.
In addition, other factors that can contribute to the development of folliculitis on the scalp, such as dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis or acne, for example.
Types of scalp folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis can be classified according to its cause, the main ones being:
1. Infectious folliculitis
Infectious folliculitis on the scalp can be classified according to the microorganism that caused the infection, such as
- Bacterial folliculitis: caused by bacteria, such as Cutibacterium acnes, Pseudomonas or Staphylococcus aureus;
- Fungal folliculitis: caused by fungi of the species Malassezia, Trichophyton, Microsporum or Candida;
- Parasitic folliculitis: caused by mites, such as Demodex follicles;
- Viral folliculitis: caused by viruses, such as herpes simplex or shingles.
Depending on the type of microorganism causing it, folliculitis on the scalp can be superficial or deep, and the person may also present symptoms, such as nodules, lumps or abscesses, or even bumps on the back of the neck or behind the ears, or fever.
Since folliculitis is caused by fungi, bacteria, mites or viruses, it can be contagious.
2. Non-infectious folliculitis
Non-infectious folliculitis is not caused by infections by microorganisms and is not contagious, and also has different types, such as:
- Folliculitis decalvans: In this type, inflammation and destruction of hair follicles occur. The exact cause is not fully known, but it appears to be related to an exaggerated response of the immune system to the presence of the bacteria. Staphylococcus aureus which normally lives on the skin, resulting in scar formation and hair loss and alopecia. Furthermore, this type of folliculitis can also be triggered by bacterial folliculitis due to S. aureus;
- Dissecting folliculitis: It is caused by inflammatory reactions, usually due to hidradenitis or acne conglobata, resulting in nodules, lumps or abscesses on the scalp that can lead to hair loss that can be permanent.
Additionally, another type is neck keloid folliculitis, which is more common in men who have thicker, curlier hair, resulting in the formation of keloids along the hairline and hair loss.
3. Perifoliculite
Perifoliculitis is inflammation around the hair follicle and its cause is not fully known, however, it is more common in young black men, and is usually associated with recurrent bacterial infections, hidradenitis suppurativa, acne conglobata or spinal arthritis.
This type of folliculitis on the scalp is rare but serious, and can form large nodules, cysts and abscesses with pus, and lead to hair loss or the formation of scars.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment of hair folliculitis must be carried out under the guidance of a dermatologist and varies according to its cause and type, and generally involves the use of medication.
The main remedies for treating scalp folliculitis that may be recommended by your doctor are:
- antibacterial soap, if folliculitis is located along the hairline;
- Shampoo anticaspa, such as ketoconazole or ciclopirox olamine;
- Antibiotics, such as clindamycin, erythromycin, metronidazole or tetracycline in the form of ointments or tablets;
- Corticosteroid ointmentssuch as betamethasone;
- Antifungalssuch as itraconazole and fluconazole in the form of ointments or tablets;
- Retinoidessuch as isotretinoin, in some cases.
Additionally, in some cases the doctor may perform surgery to drain pus from abscesses on the scalp. See all treatment options for folliculitis.
Home remedy for scalp folliculitis
A good home remedy for scalp folliculitis is to apply warm compresses to the lesions several times a day.
This is because warm compresses help to alleviate symptoms and drain pus from the lesions.
How to prevent
Some ways to prevent the appearance of folliculitis on the scalp are:
- Wash your head and scalp daily with shampoos suitable for your hair type, especially after sweating;
- Avoid frequent use of hats, wigs or caps;
- Do not pull your hair too hard when braiding or braiding a ponytail, and do not do them frequently;
- Avoid sleeping with wet or tied up hair;
- Avoid shaving your hair with blades or machines in mode 0 or 1;
- Do not share personal objects such as towels, hairbrushes or combs;
- Avoid applying conditioner, oils or leave-in creams close to the hair roots;
- Avoid going to swimming pools or using bathtubs that have not been properly sanitized.
Furthermore, it is important that when symptoms of folliculitis appear on the scalp, avoid scratching or touching the lesions.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13