Exercising is important for people with diabetes, as it helps regulate blood sugar levels, reduces insulin resistance, improves the functioning of the heart and respiratory system, and helps reduce waist circumference and lose weight.
Exercise is recommended when blood glucose is below 250 mg/dL and it is recommended that they be practiced between 3 and 5 days a week, however the type of exercise may vary if the person has any of the complications of diabetes, such as retinopathy. or wounds on the feet, and fighting, for example, is not recommended in these cases.

Exercises recommended for diabetes
In diabetes, exercise should be performed moderately, 3 to 5 days a week, lasting 30 to 45 minutes per class. Training intensity should be 60 to 70% of maximum heart rate. If you want to lose weight, you need to train at least 5 days a week, at a high intensity to burn fat.
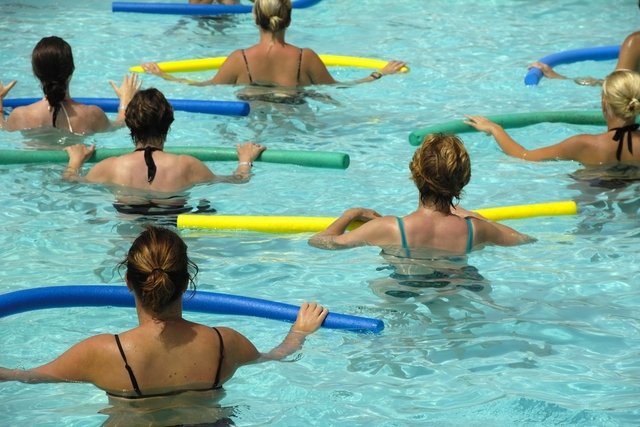
Diabetics can practice any type of physical exercise, as long as they have blood glucose levels below 250 mg/dL and do not have eye problems, such as diabetic retinopathy, or wounds on their feet. In these cases, it is not recommended to do exercises such as fighting or those involving jumping. If you have wounds on your feet, you can do exercises such as cycling or in water, such as swimming or water aerobics.
Other exercises that may be recommended when there are no complications are brisk walking, running, weight training, Pilates with a ball, equipment or on the floor, dance classes, or in a group. But it is not recommended to exercise alone to avoid the risk of having an episode of hypoglycemia and not having anyone around to help if necessary.
When not to exercise
You should not exercise when your blood glucose is higher than 250 to 300 mg/dL, and after drinking alcoholic beverages, vomiting or an episode of diarrhea. You should also not train during the hottest times of the day and avoid extreme sports, as they encourage rapid changes in blood sugar.
Main benefits
Practicing some type of physical activity regularly brings great benefits to diabetics, because this way it is possible to improve blood glucose control and avoid complications resulting from diabetes. The biggest benefits of exercise for diabetes are:
- Decrease blood sugar levels;
- Improve the function of pancreas cells;
- Decrease insulin resistance, making it easier for it to enter cells;
- Improve blood circulation and blood capillaries, reducing cold feet and hands and diabetic foot;
- Improve cardiac and respiratory function, muscles and strengthen bones;
- Helps you lose weight and reduce your abdomen.
But to achieve all these benefits you need to exercise regularly, at least 3 times a week, for 30 to 45 minutes, for life. The benefits can be noticed from the 1st month of classes, however, to burn fat you need to increase the intensity and frequency of exercises, going up to 5 days a week, for 1 hour of intense training.
How to avoid hypoglycemia during exercise
To avoid hypoglycemia during exercise, you should drink 1 glass of orange juice, half an hour before class starts, if your last meal was more than 2 hours ago. It is also important to drink water or an isotonic drink during exercise because good hydration helps prevent rapid changes in blood sugar.
The best time to train is in the morning, after having breakfast, and never at night, to avoid hypoglycemia later, while sleeping. Training up to 2 hours after lunch or snack is also a possibility. If you feel dizzy, nauseous or unwell during exercise, you should stop, take a deep breath and drink 1 glass of juice or suck on a candy, for example.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13