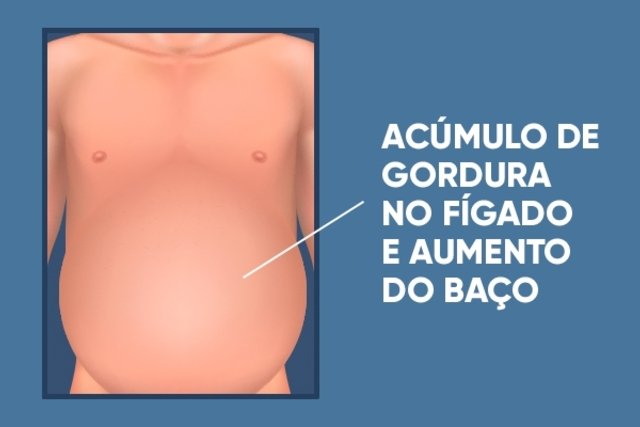
Berardinelli-Seipe Syndrome, also known as generalized congenital lipodystrophy, is a rare genetic disease that is characterized by the malfunction of the body’s fat cells, meaning that there is no accumulation of fat in normal areas of the body, but instead it is stored in other locations, such as the liver and muscles.
One of the main characteristics of this syndrome is the development of severe diabetes, which usually begins during puberty, around the age of 8 to 10. Furthermore, due to the accumulation of fat in organs, people with this syndrome have an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and serious liver and kidney problems, for example.
Treatment for this syndrome must be guided by an endocrinologist and mainly involves adopting a diet low in fats and sugars, but may also involve the use of medications according to the characteristics presented by each person.
Main symptoms and characteristics
The symptoms of Berardinelli-Seipe syndrome are linked to the reduction of normal fat tissue in the body, leading to characteristics that can appear in the first year of life, such as:
- High cholesterol and triglycerides;
- Insulin resistance and diabetes;
- Large, elongated chin, hands and feet;
- Increased muscles;
- Enlargement of the liver and spleen, causing swelling in the belly;
- Heart problems;
- Accelerated growth;
- Exaggerated increase in appetite, but with weight loss;
- Irregular menstrual cycles;
- Thick, dry hair.
In addition, symptoms such as high blood pressure, ovarian cysts and swelling on the sides of the neck, close to the mouth, may also appear. These symptoms can be observed since childhood, becoming more evident after puberty.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of Berardinelli-Seipe syndrome is made based on the evaluation of the patient’s clinical characteristics and tests that will identify changes in cholesterol values, as well as changes in the liver, kidneys and pancreas.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment is usually guided by an endocrinologist and is mainly aimed at controlling diabetes and cholesterol levels, in order to avoid serious complications from the disease. Therefore, medications such as metformin, insulin or simvastatin can be used.
A diet low in fat and rich in omega-3 should also be followed to help control cholesterol, in addition to controlling the consumption of sugar and simple carbohydrates, such as rice, flour and pasta, to help control diabetes and prevent the onset of diabetes. of other complications. See what to eat with diabetes.
Possible complications
Complications of Berardinelli-Seipe syndrome depend on the follow-up of treatment and the patient’s body’s response to the medications used, which can lead to excess fat in the liver and cirrhosis, accelerated growth in childhood, precocious puberty and cysts in the bones, causing frequent fractures.
Furthermore, diabetes in this disease often leads to serious complications if not treated correctly, such as vision problems, kidney problems and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13