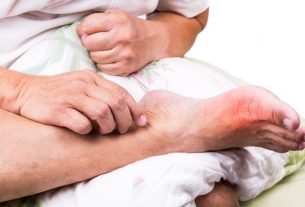
Occupational dermatosis is any change in the skin or its appendages that is directly or indirectly related to the professional activity performed or the work environment, and may be caused by temperature variations, exposure to microorganisms and contact with chemical agents, such as rubber, derivatives of petroleum and acids, for example.
Depending on the activity performed and the work environment, there may be the development of different types of occupational dermatosis, such as ulcerations, contact dermatitis caused by irritating agents, nail dystrophy and photosensitization contact dermatitis, and the treatment indicated by the dermatologist may be different from according to the dermatosis presented by the person. Find out more about dermatosis and what to do.
Main symptoms
Symptoms related to occupational dermatosis vary according to the cause, however, in general, the person may experience wounds, burns, blisters or ulcers on the skin, redness and itching of the skin, irritation, redness and watering of the eyes, runny nose and difficulty to breathe and shortness of breath.
Causes of occupational dermatosis
The causes of occupational dermatosis may be directly or indirectly related to the work environment and activity carried out, with a greater predisposition for it to occur in younger people who do not have as much professional experience and care necessary for the activity, in people who are predisposed to dermatoses not necessarily related to work and when the environment is not suitable, with no security measures, for example.
The causes of occupational dermatosis are related to the work activity performed, the main ones being:
- Contact with biological agents, such as bacteria, fungi, parasites, viruses or insects;
- Exposure to physical agents, such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, heat, cold, electricity, lasers or vibrations;
- Exposure to chemical agents, such as rubber, petroleum derivatives, cement, solvents, detergents, acids or epoxy resin,
- Contact with allergenic substances;
- Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity.
The diagnosis of occupational dermatoses must be made by a work doctor, general practitioner or dermatologist according to the symptoms presented and assessment of the relationship between the dermatosis and the activity performed. Often the diagnosis is not made because the person does not want to see a doctor and runs the risk of being suspended from work, especially because occupational dermatoses are not mandatory to report. In this way, symptoms may worsen and, consequently, harm the person.
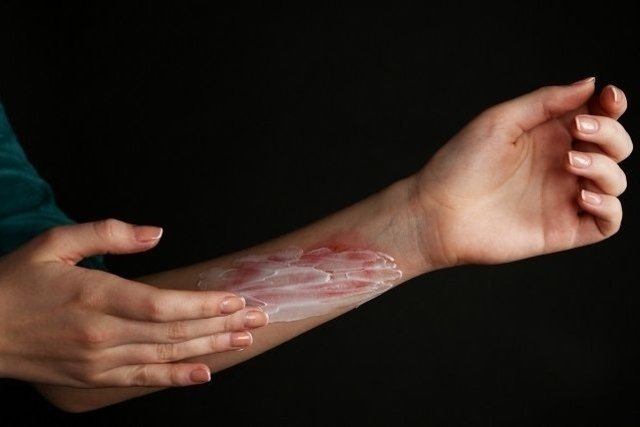
How should the treatment be
The treatment of occupational dermatosis varies according to the agent responsible for the dermatosis and the severity of the symptoms, and it is important that the dermatologist is consulted so that the symptoms of the dermatosis can be assessed and the most appropriate treatment can be indicated, which may be with the use of ointments and creams and medicines, for example. In addition, it may be recommended to adapt work materials, use personal protective equipment and stay away from work until the signs and symptoms of the dermatosis have been treated.
How to prevent occupational dermatoses
To prevent the occurrence of dermatoses, the work environment must be considered safe, in addition to being important that personal protective material is provided by the company for each worker according to the activity performed, as this makes it possible to avoid contact or exposure. to potential factors related to dermatosis.
Furthermore, it is important that the company has a collective protection plan, which involves measures that transform the working environment into a safe environment, such as adequate ventilation, isolation of risk areas and automation of processes that pose a high risk of contamination to people.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13