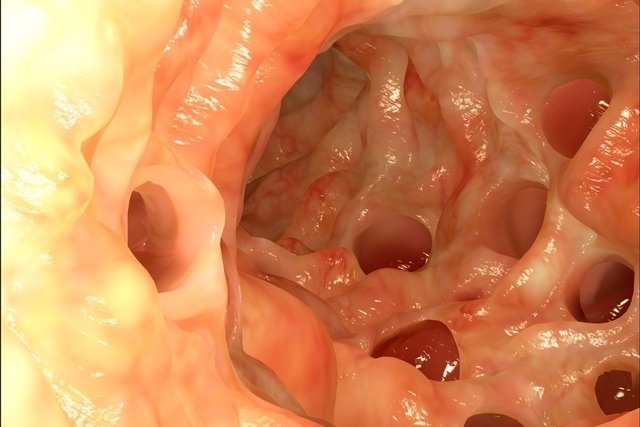
Diverticulitis is the inflammation and/or infection of diverticula, which are small pockets or sacs present in the walls of the intestine, especially in the last portion of the colon.
Diverticula are generally present in adults over 40 years of age and are more common in people who have chronic constipation or who follow a low-fiber diet. Diverticulitis can be noticed through some symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain, for example.
It is important that acute diverticulitis is identified and treated according to the gastroenterologist’s guidance, as this makes it possible to prevent complications such as intestinal perforation or obstruction.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of diverticulitis are:
- Abdominal pain, especially in the lower part of the left side;
- Periods of diarrhea or constipation;
- Tenderness on the left side of the abdomen;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Fever;
- Chills;
- Blood in the stool, in some cases;
- Loss of appetite.
The intensity of diverticulitis symptoms varies according to the severity of the inflammation, which, if it is mild, may go unnoticed.
Symptom Test
To find out the risks of having diverticulitis, select the symptoms presented in the test below:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace a consultation with a gastroenterologist.
How to confirm the diagnosis
In the presence of symptoms indicative of diverticulitis, it is important to consult a proctologist or gastroenterologist to assess the signs and symptoms presented by the person. In addition, the doctor may order imaging tests such as an ultrasound or tomography of the abdomen, and blood tests that detect inflammation and infection in the intestine, so that it is then possible to indicate the appropriate treatment to prevent complications.
Make an appointment with the nearest gastroenterologist, using the following tool, to have an evaluation carried out and check for the possibility of diverticulitis:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Causes of diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is the inflammation of the diverticula that can appear in the final portion of the colon, and may be a consequence of aging, such that there is a loss of elasticity in the intestinal muscles, allowing small pieces of feces to remain in place and leading to inflammation of the diverticulum.
Furthermore, other situations that can favor the inflammation of these structures are a diet low in fiber and chronic constipation, which leads to the formation of poorly hydrated stools, which increases pressure in the intestine and favors inflammation of the diverticula.
Due to the presence of small portions of feces, it is also possible that local infection may occur, which also causes the signs and symptoms of acute diverticulitis to appear.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for acute diverticulitis must be guided by the gastroenterologist according to the intensity of the symptoms and the cause of the inflammation, and the use of analgesic and anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended to alleviate symptoms, and antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole, to treat or prevent the development of infections.
In addition, the doctor may recommend care with your diet, which should be liquid for the first 3 days, and only then gradually add solid foods, so as not to increase the pressure inside the intestine. As the inflammation and symptoms decrease, the patient should introduce foods rich in fiber into their daily meals, such as fresh fruits and vegetables or whole grains, for example, in order to prevent the diverticula from becoming inflamed again. Check out more details about nutrition for acute diverticulitis.
When the person is able to follow the instructions well and when the condition is mild, this treatment can be done at home, however, in the case of complicated acute diverticulitis, it is important to be hospitalized to administer medication to the vein and evaluate the possibility of surgery. .
For surgical treatment of inflammation, a puncture can be performed to drain the pus or surgery to remove the affected part of the intestine. See more details about treatment and surgery options for diverticulitis.
Possible complications
When diverticulitis is not treated as soon as the first symptoms appear or when treatment is not carried out according to the doctor’s instructions, some complications may arise, such as:
- Bleedingwhich can be intense and be noticed through the presence of bright blood in the stool;
- Abscess at the site, which can cause a lot of pain and increases the risk of developing more serious infections;
- Fistula formationwhich are communications between the intestine and other organs, which originate due to inflammation and the formation of wounds in the walls;
- Bowel perforationwhich is a serious complication of diverticulitis and causes intense inflammation of the abdominal region;
- Bowel obstructionin which inflammation prevents the passage of liquids and feces through the intestine, which causes bloating, abdominal cramps and vomiting.
Therefore, to avoid these complications, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations to reduce inflammation and avoid possible complications and new attacks of acute diverticulitis.
How to avoid diverticulitis
To prevent the formation of diverticula in the large intestine, or prevent new attacks of diverticulitis, it is important to have a diet rich in fiber, as it stimulates the functioning and cleaning of the intestine, and prevents its walls from becoming weakened and new folds from forming.
For good bowel function, it is also very important to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day, on average 2 liters of water, in addition to eating slowly and chewing well before swallowing.
Also watch other tips from the nutritionist for correct nutrition during and after diverticulitis treatment, to prevent new attacks and improve bowel function

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13