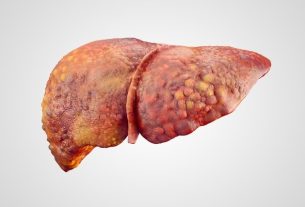
Liver cirrhosis is chronic inflammation of the liver characterized by the formation of nodules and fibrotic tissue, which make it difficult for the liver to work.
Cirrhosis is normally considered an advanced stage of other liver problems, such as hepatitis or steatosis, as there must be frequent lesions for cirrhosis to appear. In addition to these problems, cirrhosis can also develop due to excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of some medications and even due to some viral infections.
There is no cure for liver cirrhosis and, therefore, treatment usually involves changes to the diet, as well as the use of medication to control some of the symptoms. In more serious cases, liver transplant surgery may be necessary.

Main symptoms
At an early stage, cirrhosis usually does not cause symptoms. However, as liver damage increases, symptoms such as:
- Weakness and excessive tiredness;
- General malaise;
- Frequent nausea;
- Loss of appetite;
- Red spots on the skin, with small spider veins;
- Loss of weight and muscle mass;
- Pain on the right side of the abdomen, which may radiate to the lower part of the rib.
In more advanced cases of cirrhosis, it is common to observe signs such as yellowed skin and eyes, a swollen belly, very dark urine, whitish stools and itching all over the body.
When identifying any symptoms that may indicate a liver problem, it is very important to consult a hepatologist or a general practitioner, as the sooner the diagnosis is made, the easier the treatment will be.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of liver cirrhosis begins with an assessment of the symptoms presented, as well as the person’s lifestyle habits and health history.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may request laboratory tests to evaluate liver function, such as measuring the liver enzymes TGO and TGP and gamma-GT, which are elevated when the liver is damaged. In addition, tests may be requested to assess the function of the kidneys and blood clotting, as they are influenced by the functioning of the liver. See the main tests that evaluate the liver.
The doctor may also request imaging tests such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging with the aim of evaluating the liver and abdominal region, making it possible to identify injured regions and indicate the need for a biopsy, for example. Liver biopsy is not done for diagnostic purposes, but rather to determine the severity, extent and cause of cirrhosis.
Make an appointment with your nearest doctor to assess your risk of liver cirrhosis:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Possible causes
The causes of liver cirrhosis can be diverse, however, the most common are:
1. Viral hepatitis B and C
Hepatitis B and C are diseases caused mainly by viruses and are transmitted through sexual contact or sharing contaminated objects, such as needles, syringes, manicure pliers or contaminated tattoo devices. These types of hepatitis affect liver cells and, if not treated early, can cause chronic inflammation, leading to cirrhosis. Find out more about this type of hepatitis and how to prevent it.
2. Consumption of alcoholic beverages
Excessive use of alcoholic beverages can cause immediate consequences for the body, such as difficulty maintaining balance and loss of coordination. However, if consumed many days a week and in amounts above 60 g of alcohol per day, in men, or 20 g, in women, it can cause liver cirrhosis.
3. Metabolism disorders
Some metabolic disorders can lead to the appearance of liver cirrhosis, such as Wilson’s disease. This disease is rare, genetic and has no cure and is characterized by the body’s inability to metabolize copper, with accumulation in several organs, mainly the brain and liver, which can cause serious damage to these organs. Learn more about the symptoms of Wilson’s disease.
4. Fatty liver
Fatty liver, known scientifically as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver due to poor eating habits. This disease usually causes no symptoms and is most often discovered by chance. However, if left untreated, fatty liver can cause chronic inflammation of the liver, increasing the risk of cirrhosis. See what causes the accumulation of fat in the liver.
5. Use of medications
Some medications, if used excessively and regularly, can cause liver inflammation, because when they are in large quantities in the body, the liver cannot quickly metabolize these substances. Some examples of medications that can lead to the appearance of liver cirrhosis are isoniazid, nitrofurantoin, amiodarone, methotrexate, chlorpromazine and diclofenac sodium.
6. Chronic cholestasis
Chronic cholestasis is a condition in which bile cannot be carried from the liver to a part of the intestine, which may be due to obstruction of the bile ducts due to the presence of tumors, gallstones or due to a deficiency in bile production. Chronic cholestasis can lead to liver cirrhosis and is more common in people who have ulcerative colitis, which is an inflammatory bowel disease.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for cirrhosis varies according to the cause, and can involve stopping medication or alcohol, for example. Furthermore, it is important to maintain an adequate diet that includes vitamin supplementation, as due to liver impairment, the person may have difficulty digesting fats correctly. Find out what a cirrhosis diet should be like.
Depending on the symptoms presented, the hepatologist may also prescribe the use of some medications, such as diuretics, antihypertensives or creams for itchy skin, in order to improve the quality of life of the person with cirrhosis.
In the most serious cases, where there are many lesions in the liver, the only form of treatment may be liver transplantation, which is done by removing the liver with cirrhosis and placing a healthy liver from a compatible donor. See more details about the main ways to treat cirrhosis.
Possible complications
Possible complications of liver cirrhosis are portal hypertension, enlarged spleen, increased risk of infection, hemorrhage, accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, hepatorenal syndrome, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis or hepatic encephalopathy.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13