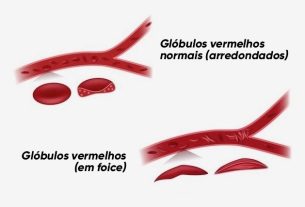
Anemia is a disease characterized by a decrease in hemoglobin in the bloodstream, which can have several causes, such as medication use, nutritional deficiencies, poor diet, genetic and autoimmune changes.
To identify and confirm the diagnosis of anemia, the doctor usually orders a blood test to assess the amount of hemoglobin, and anemia is considered when the value is less than 12 g/dL in women or 13 g/dL in men. In addition, other tests may be indicated to identify the type of anemia, such as reticulocyte count, iron and ferritin measurement and hemoglobin electrophoresis, for example. Know the tests that confirm anemia.
Regardless of the type of anemia, it is important that treatment is started, as this can reduce the risk of developing complications that result in irreversible brain damage, such as dementia, stroke and cardiovascular problems, for example.
Main types
The main types of anemia are:
1. Iron deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is one of the most common types of anemia and occurs mainly due to a decrease in the consumption of foods rich in iron, such as red meat, eggs or spinach. However, this type of anemia can also appear after bleeding or severe menstruation, due to the loss of iron from the blood.
Due to the decrease in the amount of iron, it is possible to observe a decrease in the amount of circulating hemoglobin, as iron is essential for the formation of hemoglobin, causing symptoms such as tiredness, weakness, drowsiness, feelings of dizziness or fainting, weak and brittle nails , dry skin and hair loss. See more about iron deficiency anemia.
How to deal with: The treatment of iron deficiency anemia must be guided by a doctor and may involve changes in eating habits, with an increase in the consumption of foods rich in iron and, in some cases, the use of an iron supplement may be indicated. In more serious cases, a blood transfusion may be recommended.
2. Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is a type of anemia characterized by a change in the shape of red blood cells, which take on a sickle or half-moon shape, interfering with the amount of hemoglobin that may be present within the red blood cells, causing symptoms such as excessive tiredness, paleness, generalized pain , swelling of the feet and hands, and yellowing of the eyes and skin. Learn more about sickle cell anemia.
How to deal with: Treatment for sickle cell anemia aims to alleviate symptoms, as there is no cure for this type of anemia. Therefore, the hematologist may recommend the use of analgesic and anti-inflammatory medications, as well as blood transfusion in some cases.
3. Megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia that occurs due to a reduced intake of vitamin B12 or folic acid, and is more common in people who follow a vegetarian diet, or is a consequence of the use of some medications.
Thus, due to nutritional deficiencies and the development of anemia, symptoms such as abdominal pain, hair loss, tiredness and mouth sores may be noticed. Check out other symptoms of megaloblastic anemia.
In this type of anemia, the red blood cells become larger than normal, and there may be a decrease in the number of circulating red blood cells, and a decrease in the number of circulating platelets and white blood cells is also observed.
How to deal with: The treatment of megaloblastic anemia must be guided by the doctor, together with the nutritionist, who must make adjustments to the diet to increase the consumption of foods rich in folic acid and/or vitamin B12, depending on the cause of the anemia. In some cases, the use of a dietary supplement may also be indicated.
If megaloblastic anemia is caused by the use of medication, the doctor may recommend suspending, changing the dose or changing the medication.
4. Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of megaloblastic anemia that occurs when a person ingests vitamin B12, but the body is unable to absorb it due to the absence or decrease in the amount of a protein responsible for binding to vitamin B12 and promoting its absorption, which intrinsic factor.
This type of anemia is more common in people who have celiac disease, childhood malnutrition or homocystinuria, for example, causing symptoms such as weakness, headache, excessive tiredness, heart palpitations and dizziness. In more serious cases, there may also be involvement of the nervous system. Learn more about pernicious anemia.
How to deal with: Treatment for pernicious anemia must be guided by a doctor and is normally done with the application of vitamin B12 injections or the use of a vitamin B12 supplement. Furthermore, it is important to add more foods rich in vitamin B12 to your daily diet, such as meat, eggs and cheese, for example. Check out a list of foods rich in vitamin B12.
5. Anemia de Fanconi
Fanconi anemia is a rare type of genetic anemia characterized by congenital changes and a progressive decrease in the functioning of the bone marrow, so that a decrease in the production of blood cells is noted.
In this way, the characteristic symptoms of anemia can be noticed, such as excessive tiredness, weakness, dizziness and paleness, in addition to the possibility of deformity in the bones, changes in vision, red spots on the skin and a greater risk of developing cancer. Know how to recognize the symptoms of Fanconi anemia.
How to deal with: The treatment of Fanconi anemia must be guided by a hematologist and involves the use of corticosteroid medications and/or blood transfusions. In more serious cases, a bone marrow transplant may be recommended.
6. Thalassemia
Thalassemia is a type of anemia that is caused by genetic changes that lead to defects in the hemoglobin synthesis process, which can cause fatigue, irritability, growth retardation, lack of appetite and weakening of the immune system, for example.
Thalassemia can be classified into some types according to the hemoglobin chain that has had its development impaired, which can cause the symptoms presented by the person to be less or more severe. Learn how to identify each type of thalassemia.
How to deal with: It is important to identify the type of thalassemia so that treatment can be initiated and, thus, the progression of the disease can be prevented. Furthermore, it is important to follow an adequate diet to improve quality of life and ensure a feeling of well-being.
7. Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia is a type of autoimmune anemia in which the body itself produces antibodies against blood cells, causing their destruction, causing symptoms such as paleness, dizziness, purple marks on the skin, dry and yellowish skin and eyes, dark urine and swelling abdominal. See other symptoms of this type of anemia.
How to deal with: The treatment of hemolytic anemia must be guided by a hematologist, and the use of corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and immunomodulators may be recommended, and blood transfusion and spleen removal may also be recommended in some cases.
8. Aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia is a type of anemia in which the bone marrow progressively decreases the production of blood cells, which can happen due to the use of medications, autoimmune diseases, infection or frequent exposure to toxic substances.
Thus, due to the decrease in the number of blood cells, symptoms such as purple spots on the skin, bleeding that can take a long time to stop, shortness of breath, headache, pale skin and mucous membranes can be noticed.
How to deal with: in this case, the doctor may recommend a blood transfusion and the use of medications that stimulate the functioning of the bone marrow and/or immunosuppressants. In some cases, a bone marrow transplant may also be recommended. See more details on the treatment of aplastic anemia.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13