Treatment for osteoarthritis can be done with the use of medication, physiotherapy, exercise and in more serious cases when symptoms persist, making life difficult for the person, surgery may be indicated, but as a last resort.
Symptoms are normally well controlled with anti-inflammatory tablets such as Ibuprofen, but as these should not be taken for more than 7 days as they cause stomach pain, the doctor may also recommend the daily application of anti-inflammatory ointments to apply to the area of pain.
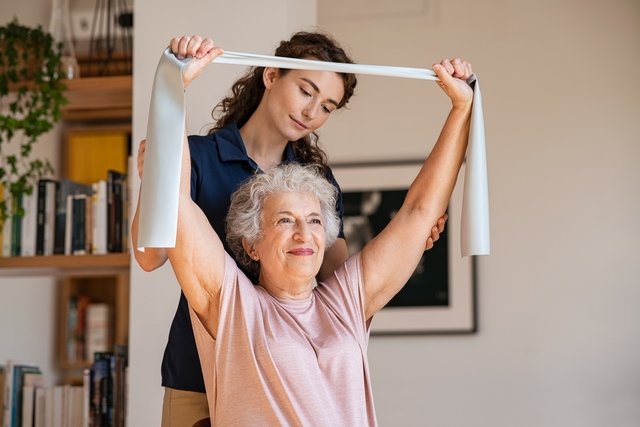
Physiotherapy is a great ally and is useful for pain relief, reducing swelling, noise when moving the joint and improving function, being recommended for everyone. When combined with medications, they are very effective in relieving pain and improving function.

Thus, the treatments available for osteoarthritis include:
1. Medicines
Remedies for osteoarthritis must be prescribed by the orthopedist, and the use of analgesic and anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended, such as, for example, Paracetamol, Aspirin, Ibuprofen and Naproxen to relieve pain and swelling of the joints or the application of Moment ointment. or Voltaren. Another medicine used in osteoarthritis is Artrolive or Condroflex, which contain two substances that help regenerate joint cartilage, protecting them from degeneration. See more details about osteoarthritis remedies.
When these medications combined with physiotherapy do not have the expected effect and the pain is disabling, the doctor may prescribe an infiltration with anesthetic, corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid directly into the affected joint.
2. Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment for osteoarthritis aims to reduce pain and discomfort through the use of physiotherapy devices, thermal resources such as heat or ice packs and mobilization and strengthening exercises. This prevents the cartilage from being further destroyed, increasing the intra-articular space through exercises and mobilizations. Find out how physiotherapy for osteoarthritis can be done.
Strengthening the muscles that surround the affected joint is essential so that this joint is a little more protected and causes less pain, which is why it is recommended to practice the exercises recommended by the physiotherapist, both in the clinic and at home. Discover some exercises for knee osteoarthritis.
Cycling, on the treadmill and doing Pilates are also good options when there is no pain to maintain strength, being useful to reduce the early return of symptoms.
3. Surgery
Surgery is indicated when the use of medications and physiotherapy are insufficient to alleviate the pain and limitations that the individual presents. It should always be the last therapeutic option, as it can leave permanent sequelae, such as loss of range of motion in the affected joint.
Surgery can be done to scrape the affected tissue or replace part or all of the joint. After the procedure, the person still needs to undergo physical therapy for a few more weeks until the tissue is completely healed and there is no need to use crutches or other devices to aid movement and until the person is able to carry out their daily activities normally.
4. Natural treatment
A good natural treatment for osteoarthritis is the consumption of sucupira seed tea, as this medicinal plant has a calming and regenerating effect on joints, being useful to complement clinical and physiotherapeutic treatment. For tea, it is recommended to boil 12 crushed sucupira seeds in a liter of water and drink several times during the day.
5. Home treatment
A good home treatment for osteoarthritis is to place a hot water bottle on the affected joint when it hurts. To achieve the same objective, place a cloth bundle stuffed with sesame or flax seeds heated in the microwave on top of the joint to reduce pain and discomfort. It is recommended to leave it on for approximately 15 to 20 minutes. See more options for home remedies for osteoarthritis.
Signs of improvement and worsening
The reduction in swelling, pain and improvement in function are the first signs of improvement in osteoarthritis, but as these symptoms persist, the condition worsens and it is necessary to investigate what may be happening through imaging tests such as rays. x or MRI.
Complications of osteoarthritis
Complications arise when treatment is not carried out, resulting in an increase in the intensity and frequency of pain. This may indicate a progression of osteoarthritis, with a larger affected area and sometimes only surgery to place a prosthesis can bring relief of symptoms.
Care in case of osteoarthritis
Regardless of the treatment chosen by the doctor and the patient in agreement, it is essential that the individual follows some recommendations to enhance the treatment, such as:
- Lose weight, if you are above the ideal weight for your height and age;
- Eat healthily, giving preference to the consumption of anti-inflammatory foods;
- Drink plenty of water to help with joint lubrication and skin and muscle flexibility;
- Rest whenever you feel pain in your joints;
- Avoid making efforts;
- Wear appropriate clothing and shoes that are light and comfortable.
Furthermore, it is recommended to avoid repetitive movements with the diseased joint. For example: anyone who has osteoarthritis in their hands or fingers should avoid knitting, crocheting or washing clothes by hand, and anyone who has osteoarthritis of the spine should avoid climbing stairs or constantly getting up and down.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13