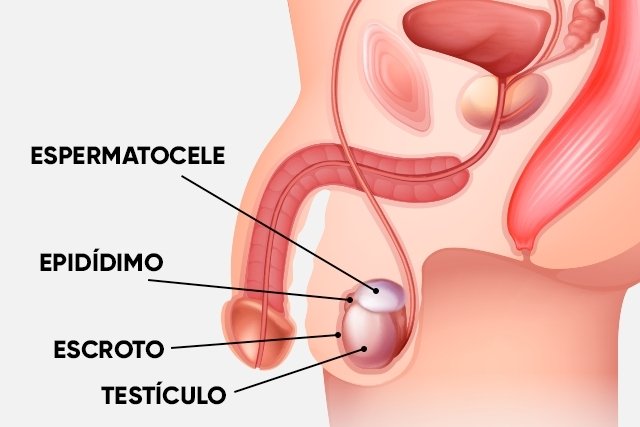
Spermatocele is a small, painless cyst that appears in the epididymis, which is the place where the canal that transports sperm connects to the testicle, which can cause a feeling of heaviness in the region and pain and discomfort on the side of the affected testicle, especially when the cyst is big.
Spermatocele, also known as seminal cyst or epididymal cyst, is normally identified when palpating the testicles during bathing, and it is important that the doctor is consulted as soon as any changes are identified.
Although it is almost always benign, this change should always be evaluated by a urologist, as this type of change can also be a sign of a malignant tumor, even in rarer cases. Normally, spermatocele does not reduce a man’s fertility and therefore may not require treatment.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of spermatocele are:
- Appearance of a cyst next to the testicle;
- Cyst that does not hurt, but can be moved;
- Pain or discomfort on the side of the affected testicle;
- Sensation of heaviness in the intimate region.
When any change in the testicle is identified, even if there are no other symptoms, it is very important to consult a urologist to rule out other more serious causes, such as torsion of the testicle or even cancer, for example.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of spermatocele is made by the urologist through a physical examination, in which the man’s intimate region is observed and palpated to verify the presence of the cyst, in addition to evaluating other symptoms presented by the person.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Furthermore, to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor can perform transillumination, which consists of illuminating the scrotum region so that it is possible to better assess the location, and ultrasound may also be recommended to identify the presence of the cyst.
Possible causes
The causes of spermatocele are not yet fully known, but it is believed to occur due to a blockage in the tubules present in the epididymis that are responsible for transporting sperm. Thus, this situation could be favored by some situations, such as epididymitis, having a vasectomy or a strong blow to the area.
How the treatment is carried out
Since most spermatoceles do not cause any type of complication or discomfort, no type of treatment is generally necessary. However, the urologist can schedule frequent appointments, around twice a year, to assess the size of the cyst and ensure that it is not undergoing changes that could indicate malignancy.
If spermatocele causes discomfort or pain during everyday life, the doctor may prescribe the use of anti-inflammatories to reduce the local inflammatory process. After using these remedies for 1 or 2 weeks, the symptoms may disappear completely and, if this happens, no further treatment is necessary. However, if symptoms persist, evaluation may be necessary to perform minor surgery.
Surgery for spermatocele
Surgery to treat spermatocele, also known as spermatocelectomy, is normally performed under general anesthesia and allows the doctor to separate and remove the spermatocele from the epididymis. After surgery, it is usually necessary to use a type of “scrotal suspender” that helps maintain pressure in the area, preventing the cut from opening when moving, for example.
During recovery, it is still recommended to take some precautions, such as:
- Apply cold compresses in the intimate region;
- Taking prescribed medications by the doctor;
- Avoid wetting the intimate area until the stitches are removed;
- Treat the wound at the health center or hospital.
Although it is rare, some complications may arise after surgery, especially infertility if there is any damage to the epididymis and/or vas deferens. Therefore, it is very important to select a certified urology clinic with a highly experienced surgeon.
Bibliography
- UROLOGY CARE FOUNDATION. What are Spermatoceles (Spermatic Cysts)?. Available at: <https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-az/s/spermatoceles>. Accessed on April 12, 2023
- MAYO CLINIC. Spermatocele. Available at: <https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/spermatocele/symptoms-causes/syc-20377829>. Accessed on April 12, 2023
- NATIONAL TOXICOLOGY PROGRAM. Epididymis – Spermatocele. Available at: <https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/nnl/male_reproductive/epididymis/spermatocele/epididymis_spermatocele_508_pdf.pdf>. Accessed on April 12, 2023

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13



