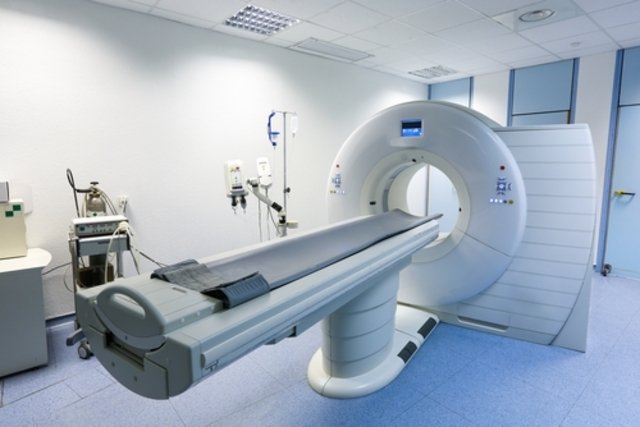
Computed tomography (CT) is an imaging test that uses X-rays to generate detailed images of the inside of the body, allowing bones, organs or other types of tissue to be observed, in order to identify health problems such as tumors, aneurysms or infections , for example.
This exam does not cause pain and anyone can perform it, however, pregnant women should preferably undergo other exams as an alternative, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, as exposure to radiation is greater in tomography.
The tomography can be performed with or without the use of contrast, which is a type of liquid that can be swallowed, injected into a vein or inserted into the rectum, during the exam, to facilitate the visualization of certain parts of the body, it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions related to preparation for contrast tomography.
What is it for
Computed tomography is used to:
- Help in the diagnosis of muscle and bone diseases;
- Identify the location of a tumor, infection or clot;
- Determine the size of a tumor;
- Assess metastasis;
- Detect and monitor illnesses and injuries;
- Monitor response to disease treatment.
Computed tomography makes it possible to differentiate the different types of tissue and thus provide more detailed images of the organs that cannot be clearly observed through an x-ray.
Despite being an exam with high sensitivity and image quality, tomography should not be considered the first exam option, at least in most cases, as it exposes the body to radiation.
Make an appointment with your nearest doctor to assess the need for a CT scan:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
Difference Between CT Scan and MRI
Both computed tomography allows you to differentiate tissues and visualize organs in detail. However, while CT uses ionizing radiation to obtain images, MRI uses a high-intensity magnetic field. Understand better how MRI is performed.
Main types of computed tomography
The main types of tomography are:
- Skull tomography: indicated for investigation of trauma, infections, occurrence of hemorrhage, hydrocephalus or presence of aneurysms;
- Tomography of the abdomen and pelvis: requested to evaluate the evolution of tumors and abscesses, in addition to checking the occurrence of appendicitis, lithiasis, renal malformation, pancreatitis, pseudocysts, liver injuries, cirrhosis and hemangioma.
- Tomography of upper and lower limbs: used for muscle injuries, fractures, tumors and infections;
- Chest tomography: indicated for investigating infections, vascular diseases, tracking tumors and evaluating the evolution of tumors.
Normally CT scans of the skull, chest and abdomen are performed with contrast so that there is better visualization of the structures and it is possible to easily distinguish the different types of tissues.
How to prepare for the CT scan
Preparing for a CT scan depends on the purpose of the exam. In cases where it will be done with the administration of contrast, for example, it is recommended that the person fast for up to 8 hours, or as recommended by the doctor, so that the contrast is better absorbed and, thus, the image generated be clearer.
In cases where a tomography of the digestive area will be performed, fasting for just 4 hours or the use of laxatives to cleanse the intestine, for example, may be indicated.
Since the guidelines for CT scans vary depending on the purpose of the exam, it is important to check the guidelines with the doctor or clinic where the procedure will be performed.
However, regardless of the type of computed tomography, it is recommended to remove any object with metal, such as a bra, earrings or bracelet, as they may interfere with the results of the exam. It is also important to inform the radiology technician who will conduct the examination if you have any implanted device, such as a pacemaker, for example.
How the exam is carried out
Tomography is a simple and quick procedure that lasts, on average, less than 30 minutes. To carry out this examination, the person lies on a stretcher and must remain still throughout the examination to avoid changes in the images.
After lying on the stretcher, the examination begins by moving the stretcher to the tomograph, which is a type of tunnel, and the stretcher can be moved in and out of the tomograph during the examination according to the objective. In the tomograph, X-rays are emitted, generating images on the computer.
Computed tomography does not hurt or cause distress, as the equipment is open, unlike magnetic resonance imaging.
When it is not recommended
Computed tomography is not recommended for pregnant women or women suspected of being pregnant, as it is performed using X-rays and with contrast, in some cases.
Furthermore, in the case of people who use metformin, it is recommended to discontinue the medication to carry out this test.
Computed tomography is also not recommended for people with allergies or asthma, and it is important to discuss other alternatives for this exam.
Bibliography
- FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF GOIÁS – HOSPITAL DAS CLINICAS. Techniques for performing computed tomography exams. 2021. Available at: <https://www.gov.br/ebserh/pt-br/hospitais-universitarios/regiao-centro-oeste/hc-ufg/governanca/pops-e-protocolos/gerencia-de-atencao- a-health/diagnostic-and-therapeutic-support-division/POP.UDI.008.TcnicasderealizaodeexamesemTC.pdf>. Accessed on November 12, 2021

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13