Thyroid FNAC or Fine Needle Aspiration, is an exam recommended by the endocrinologist to evaluate the cyst or nodule found in the thyroid, being useful to check whether it has benign or malignant characteristics.
FNAB, also known as thyroid biopsy, is normally performed during or after thyroid ultrasound, in which the gland as a whole is observed and changes can be identified.
Normally, thyroid nodules that are small and benign do not require treatment, but if they are large, surgery may be necessary to remove them. In the case of malignant nodules, treatment usually involves surgery and iodine therapy. Know how to identify a thyroid nodule.
What is it for
FNAC serves to differentiate benign from malignant nodules that may be present in the thyroid. This is possible through laboratory analysis of the thyroid sample collected using a fine needle.
The thyroid nodule can be identified during a physical examination, in which the doctor palpates the thyroid gland, or by performing an ultrasound examination of the thyroid, this method being the most suitable for identifying nodules, since is associated with lower rates of non-diagnosis/false-negative results.
If you need to have a thyroid FNAC, make an appointment with an endocrinologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
When is indicated
Thyroid FNAC testing is indicated in the following cases:
- Thyroid nodule equal to or larger than 1 cm, with normal thyroid function and suspected malignancy;
- Nodules larger than 0.5 cm and suspected of being malignant;
- Increase in the thyroid nodule by more than 50% during regular medical monitoring;
- Solid nodules or cysts with microcalcifications;
- 1st degree relative with thyroid cancer;
- Exposure to radiation in childhood or adolescence;
- Nodule with apparent invasion outside the thyroid;
- Suspicious lymph node during ultrasound.
Thyroid FNAC is normally requested when the nodule shows changes during the ultrasound examination.
Furthermore, when there is more than one nodule in the thyroid, all of them must be examined, removing solid and liquid parts from all of them so that they can be analyzed in the laboratory.
How to prepare for the PAAF
Before performing the thyroid FNAC, it is recommended that the use of anticoagulant medications, such as ASA, heparin or warfarin, be suspended 3 days before the exam, or according to the doctor’s instructions.
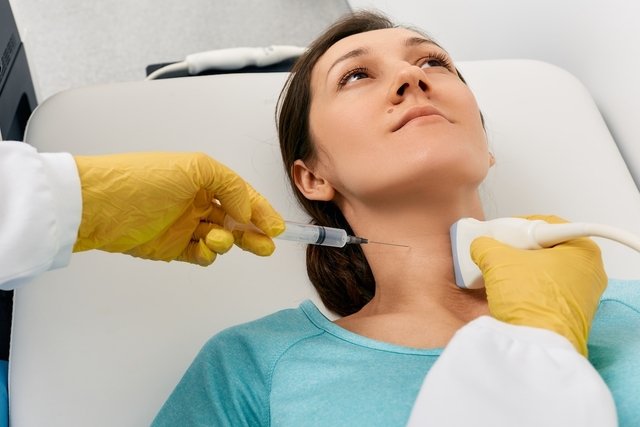
How it is made
The FNAC is performed by the endocrinologist in the doctor’s office and can also be performed at the same time as the thyroid ultrasound.
To perform the FNAC, the doctor must follow some steps, such as:
- Place the person lying down on a stretcher face up;
- Do the cleaning and skin asepsis;
- Use an ultrasound to guide the location in which you must insert the fine needle and prevent injuries during the procedure;
- Insert the fine needle attached to a syringe to remove a tissue sample or all the liquid from the nodule;
- Repeat the procedureif necessary, to remove tissue from different parts of the nodule;
- Place the collected material on a slide to send to the laboratory;
- Make a small bandage at the puncture site.
Generally, to perform FNAC, local anesthesia is not necessary, as the needle is very thin, causing only temporary discomfort. In the case of children, light sedation may sometimes be necessary.
Furthermore, general anesthesia is not indicated for performing FNAB, as the risks do not justify its use during this exam.
After the exam, the person is released to return home, without requiring hospitalization.
Care after the exam
After the thyroid FNA test, no specific care is required and the person can return to their normal routine.
It is normal for the puncture site to be a little sore for 1 or 2 days, and the doctor may recommend the use of painkillers, such as paracetamol, to reduce discomfort.
How to understand the results
PAAF results are released in a report according to the Bethesda classification, and include:
The result of the thyroid FNAC must always be interpreted by the doctor according to the classification of the nodule and its characteristics, in order to indicate the most appropriate treatment.
Possible complications
Thyroid FNAC is considered a safe test, with few complications, however, bleeding at the puncture site, hematoma, swelling, infections or damage to thyroid structures may rarely occur.
Bibliography
- TAFTI, D.; SCHULTZ, D. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Thyroid Nodule Biopsy. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557883/>. Accessed on May 31, 2023
- THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY, THE JOHNS HOPKINS HOSPITAL, AND JOHNS HOPKINS HEALTH SYSTEM. Thyroid Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy. 2023. Disponível em: <https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/thyroid-fine-needle-aspiration-biopsy>. Acesso em 31 mai 2023
- FELDKAMP, J.; et al. Fine Needle Aspiration in the Investigation of Thyroid Nodules. Dtsch Ärztebl Int. 113. 20; 353-9, 2016
- THE, AR; et al. Thyroid Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: an evaluation of its utility in a community setting. Le AR. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 44. 1; 12, 2015
- KWAK, J.Y. Indications for Fine Needle Aspiration in Thyroid Nodules. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 28. 2; 81–85, 2013
- . DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH OF THE STATE OF BAHIA. Thyroid Nodules Protocol. 2020. Available at: <http://telessaude.ba.gov.br/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Nodulos_tireoide.pdf>. Accessed on 01 Dec 2021
- GOULART, Ana Paula FE Analysis of Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) results of thyroid nodules and correlation with thyroidectomies and population in the interior of the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Master’s Thesis, 2018. University of São Paulo.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13