Electromyography is a quick and simple test that allows you to evaluate muscle function and diagnose nerve or muscle problems. This exam is usually indicated when the person has frequent tingling, weakness or muscle pain.
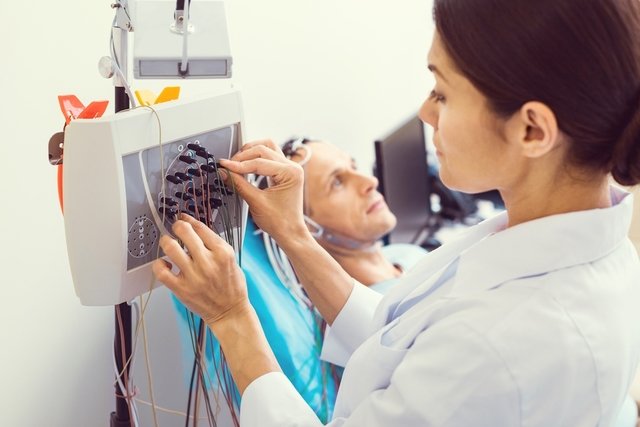
In electromyography, electrodes are placed on the muscle group that will be evaluated and an electrical current is applied to generate a response from the muscle, which is captured by the equipment used.
Electromyography is a non-invasive method that can be done in health clinics by a healthcare professional and lasts around 30 minutes.
What is it for
Electromyography is an exam carried out to evaluate the muscles, the level of muscle activation during the execution of the movement, the intensity and duration of muscle demand or to evaluate muscle fatigue.
This examination is generally carried out when the person complains of symptoms, such as tingling, muscle weakness, muscle pain, cramps, involuntary movements, changes in sensitivity or muscle paralysis, for example, which can be caused by different nervous diseases.
How to prepare for the exam
Before carrying out the exam, the person should not apply products to the skin, such as creams, lotions or ointments, so that there is no interference with the exam and so that the electrodes adhere easily to the skin. Rings, bracelets, watches and other metallic objects should also be removed.
Furthermore, if the person takes medication, they must inform the doctor, as it may be necessary to temporarily interrupt the treatment approximately 3 days before the exam, as in cases where the person is taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents.
How the exam is carried out
Electromyography is a simple and quick exam, which lasts around 30 minutes, is carried out with the person sitting or lying down, and uses equipment called an electromyograph, which is coupled to a computer and electrodes.
The electrodes are placed as close as possible to the muscle to be evaluated and then small electrical currents are applied and the muscles’ response to the applied stimuli is captured. The electrodes can also be needle electrodes, which are most commonly used to assess muscle activity at rest or during muscle contraction.
After placing the electrodes, the person may be asked to perform certain movements, in order to evaluate the response of the muscles when the nerves are stimulated. In addition, some electrical stimulation of the nerves can also be performed.
Possible side effects
Electromyography is generally a well-tolerated technique, however, when needle electrodes are used, this can cause some discomfort and muscles can become sore, and small dark spots may appear on the skin a few days after the exam.
Furthermore, although it is very rare, bleeding or infection may occur in the area where the electrodes are inserted.
Bibliography
- MACHADO, Naila AG et al. al.. Electromyography Applied to Temporomandibular Disorders. Rev Odontol Bras Central . 51. 19; 280-284, 2010
- AFFIDEA. Electromyography. Available at: <https://www.affidea.pt/services/exames-de-especialidade/neurologia/eletromiografia/>. Accessed on September 9, 2019
- SANTA MARIA HOSPITAL – PORTO. Electromyography. Available at: <https://www.hsmporto.pt/exames/electromiografia/>. Accessed on September 9, 2019
- JUNIOR, Guanis de Barros Vilela. FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTROMYOGRAPHY. Available at: <http://www.cpaqv.org/mtpmh/eletromiografia.pdf>.
- BIOPHYSICS LABORATORY, SCHOOL OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND SPORT, UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO. Instrumentation in electromyography. 2006. Available at: <http://demotu.org/pubs/EMG.pdf>. Accessed on September 9, 2019

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13