Campimetry is an exam that helps diagnose eye problems, especially glaucoma, as it allows the ophthalmologist to assess the person’s ability to perceive the central and peripheral visual field.
Campimetry, which is also known as visual field examination or ocular perimetry, can also be done to identify changes in the visual field and retinal diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration or tumors, for example.
The campimetry exam can be carried out free of charge by the SUS or in private clinics, and the results must be analyzed by the ophthalmologist, who can also request other tests to evaluate the structures of the eyes, such as the OTC test or corneal topography, for example. See other eye exams that can be done by an ophthalmologist.
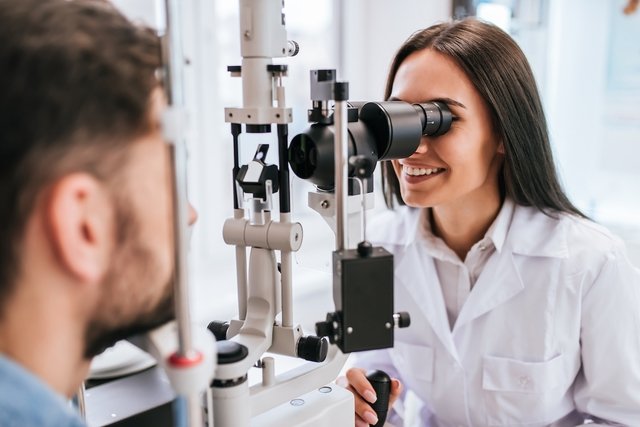

When is it indicated
Campimetry is indicated to diagnose, evaluate the evolution or response to treatment of:
- Glaucoma;
- Macular degeneration;
- Edema macular;
- Retinitis pigmentar;
- Retinose;
- Changes in the optic nerve, such as papilledema and papillitis;
- Neurological problems, such as stroke or brain tumors;
- Eye pain;
- Drug poisoning;
- Changes in the field of vision.
Furthermore, campimetry should be performed when there is a diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, high blood pressure, or pituitary gland diseases, as it allows checking whether there are changes in the visual field.
Make an appointment with an ophthalmologist in the nearest region:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How to prepare
It is not necessary to prepare to perform the campimetry exam, and it is only recommended that people who are being treated for glaucoma discontinue the pilocarpine medication approximately 3 days before the exam, in accordance with the ophthalmologist’s instructions.
Furthermore, people who wear contact lenses do not need to remove them to take the exam, but they should always remember to bring the latest medical prescription for their glasses.
How campimetry is performed
Visual campimetry is performed with the person sitting with their face glued to the measuring device, called a campimeter, which emits points of light in different places and with different intensities in the patient’s field of vision.
During the test, a light at the bottom of the device is emitted so that the person keeps their vision focused on it. Thus, the person will have to ring a bell as they manage to identify the new points of light that appear, but without moving their eyes to the sides, finding the lights only with their peripheral vision.
The campimetry exam is simple and causes no pain, lasting around 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the person’s cooperation.
Types of perimetry
According to the way the exam is performed, perimetry can be classified into three main types:
1. Computerized perimetry
Computerized perimetry, also called computerized perimetry, is performed using an electronic device, without operator interference, and generally provides a more accurate diagnosis, and can be performed in one or both eyes.
2. Kinetic perimetry
Kinetic perimetry uses equipment with a light source that remains in motion, being moved at different angles, which is perceived by the person.
3. Static campimetry
In static perimetry, the equipment with the light source remains stationary, without moving, emitting different light stimuli, and the person must click a button on the device each time they identify the brightness.
4. Campimetria manual
Manual perimetry encompasses kinetic perimetry and static perimetry, as it is performed using the commands of a trained professional.
In general, manual perimetry is indicated to identify problems in more peripheral vision and to evaluate people with great loss of visual acuity, the elderly, children or weak people, who have difficulty following the device’s commands.
Bibliography
- STEIN, JD; et al. Glaucoma in Adults-Screening, Diagnosis, and Management: A Review. JAMA. 325. 2; 164-174, 2021
- XU, M.; et al. Visual Field Progression in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 61. 6; 56, 2020
- MULLER, F.; et al. Rapid Campimetry—A Novel Screening Method for Glaucoma Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 11. 2156; 1-13, 2022
- WU, Z.; MEDEIROS, F. A. Recent developments in visual field testing for glaucoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 29. 1; 141-146, 2018
- WALL, M. Perimetry and visual field defects. Handb Clin Neurol. 178. 51-77, 2021
- BRAZILIAN GLAUCOMA SOCIETY. Brazilian Glaucoma Society Guidelines – Visual Field Assessment in Glaucoma. Available at: <https://www.sbglaucoma.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/03-DIRETRIZ-AVALIA%C3%87%C3%83O-DO-CAMPO-VISUAL.pdf>. Accessed on Aug 10, 2021
- GOMES, Isabel Maria CR Comparison of SWAP perimetry and conventional perimetry in the detection, analysis and follow-up of glaucoma. Master’s Thesis, 2016. University of Beira do Interior.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13