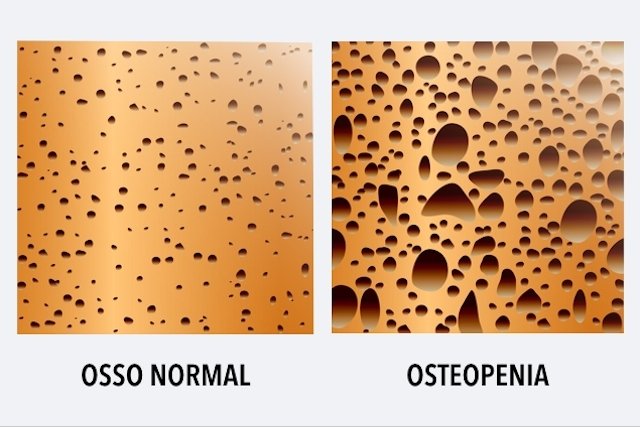
Osteopenia is the gradual decrease in bone mass, which makes bones more fragile and increases the risk of fractures. Furthermore, when osteopenia is not identified and treated correctly, it can develop into osteoporosis, where the bones are so weak and can break with just movements or small blows.
Osteopenia is more common in postmenopausal women and men over 60 years of age. This is because as we age, bones become more porous, reducing calcium absorption.
Therefore, it is recommended to practice physical activity regularly and increase the consumption of foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to avoid osteopenia and osteoporosis. Discover foods rich in calcium and vitamin D.
Main symptoms
In general, the loss of bone mass does not cause signs or symptoms. However, as bone mass is lost, bone density decreases and osteoporosis progresses, fractures and bone deformities may occur more easily in some cases.
Does osteopenia hurt?
In rare cases, osteopenia can cause pain or weakness, however when it progresses to osteoporosis, the person may have pain in the hip, neck, bones and back. Know how to recognize the symptoms of osteoporosis.
Main causes of osteopenia
Osteopenia is more common in women, especially those who went through menopause early or are postmenopausal, but it can also happen in men between 60 and 70 years old due to a decrease in testosterone production.
Furthermore, other factors that increase the risk of developing osteopenia are:
- Diet low in foods with calcium;
- Being a smoker;
- Not practicing regular physical activity;
- Have a family history of osteoporosis;
- Lack of adequate sun exposure;
- Prolonged use of medications;
- Thyroid, parathyroid, liver or kidney problems.
Furthermore, undergoing chemotherapy, alcoholism and consuming drinks or foods rich in caffeine can also promote osteopenia, because they can alter the bone formation process.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of osteopenia is made by carrying out an exam that assesses bone density, called bone densitometry. This exam is similar to an X-ray and, therefore, does not cause any pain or discomfort and the only preparation necessary is to avoid taking calcium supplements in the previous 24 hours.
Make an appointment with your nearest orthopedist to assess your risk of osteopenia:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
- Normalwhen it is equal to or greater than 1;
- Osteopeniawhen it is between 1 and -2.5;
- Osteoporosiswhen the result is less than -2.5.
This exam should be done every year by women over 65 years of age and men over 70 years of age, as osteopenia does not present any type of symptoms and, therefore, can easily evolve into osteoporosis if it is not identified and treated. Find out more about the bone densitometry exam.
Osteopenia treatment
The treatment of osteopenia aims to prevent excessive bone loss and progression to osteoporosis, and the use of medications to increase the absorption and deposition of calcium in the bones, use of calcium and vitamin D supplements and changes in eating habits may be recommended. .
1. Use of supplements and medicines
It is normally recommended by your doctor to take calcium and vitamin D supplements every day to ensure bone health.
Furthermore, in cases where the person is at greater risk of developing fractures, the doctor may recommend the use of some medications that are normally indicated for osteoporosis with the aim of increasing bone mass, such as Alendronate, Risedronate, calcitonin, Denosumab or Ranelate of Strontium, for example. See the remedies recommended for osteoporosis.
As osteopenia in women may be related to hormonal changes typical of menopause, the doctor may also recommend hormone replacement therapy, which can help rebalance metabolism and keep bones stronger for longer.
2. Practice physical activity
Lack of physical activity, especially in people who spend a lot of time in bed, is an important cause of weakening bones. On the other hand, athletes tend to have a higher bone mass than the general population.
Therefore, practicing regular physical activity is important to help restore bone strength in osteopenia, and is also a great way to prevent falls and thus reduce the risk of fractures.
In addition to practicing physical activities, it is important to adopt healthier lifestyle habits, avoiding alcohol consumption and smoking, as they can directly interfere with bone mass and increase the risk of developing osteopenia.
3. Food care
It is important that the diet in osteopenia is rich in calcium and vitamin D, as this makes it possible to maintain bone mass, making bones stronger and reducing the risk of fractures. Therefore, it is recommended to include milk, yogurt, cheese and soy, for example, in your daily diet. In addition to using supplements recommended by your doctor.
Check out the video below for other nutrition tips to keep your bones strong:

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13