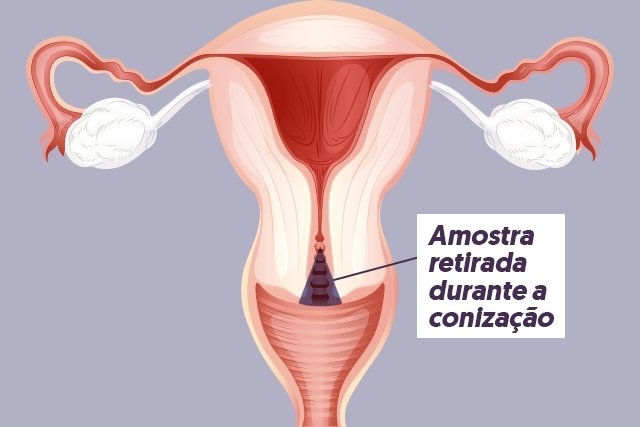
Cervical conization is a surgical procedure indicated for the diagnosis and treatment of changes in the cervix, such as dysplasia, pre-cancerous lesions, or cervical cancer in the early stages.
Generally, the gynecologist performs this procedure when there is any change identified through the preventive examination, removing a piece of the cervix, in the shape of a cone, for biopsy and, thus, being analyzed in the laboratory. See how the preventive exam is carried out.
Conization is performed by a gynecologist using local anesthesia and/or light sedation, and is offered free of charge by the SUS, or can be performed in private clinics or hospitals.
When is indicated
Conization is indicated for:
- Diagnosis of a lesion suspected of invasive cancer or an adenocarcinoma on site of the cervix;
- Assessment of lesions on the cervix when histology and cytological exams have different results;
- Diagnosis of abnormalities in the cells of the cervix, when the colposcopy examination was not sufficient to visualize the changes;
- Diagnosis of pre-malignant or malignant lesions of the cervix;
- Treatment of cervical dysplasia, CIN 2 or CIN 3;
- Treatment of early-stage squamous cell cervical cancer (1A1) if a woman wants to maintain fertility.
Conization can also be done in women with symptoms similar to cervical cancer, such as abnormal bleeding, constant pelvic pain or foul-smelling discharge, even if no tissue changes are visible. See the main symptoms of cervical cancer.
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How to prepare
Some precautions are important before carrying out conization, such as:
- Tell your doctor if you are allergic to iodine, before carrying out the procedure, as an iodine-based disinfectant solution is applied to the cervix;
- Inform your doctor about the use of anticoagulant medicationssuch as warfarin, heparin, rivaroxaban or acetylsalicylic acid, as they may increase the risk of bleeding;
- Tell your doctor if you are allergic to other medications or latex, for example;
- Fast for about 6 to 8 hoursbefore conization, if light sedation is indicated.
Furthermore, it may be recommended by the gynecologist not to have sexual intercourse for 24 hours before conization.
How conization is done
Conization surgery is quite simple and quick, lasting approximately 15 to 30 minutes.
Conization of the uterus can only be done under local anesthesia, but is often performed under light sedation and is therefore done in a surgical unit. The woman can return home the same day, without needing to be hospitalized.
During the procedure, the woman is placed in a gynecological position, with her legs open, and the doctor places the speculum at the entrance to the vagina to observe the cervix and apply an iodine-based solution to disinfect the cervix.
Then, using a small laser or a device similar to a scalpel, the doctor takes a sample of approximately 2 cm, which will be analyzed in the laboratory.
Finally, some compresses are inserted into the vagina to stop the bleeding, which must be removed before the woman returns home, or a medicine in the form of a sponge, to reduce bleeding and help with healing.
What is recovery like?
Although the surgery is relatively quick, recovery from conization can take up to 1 month to be complete and, during this period, some care is recommended, such as:
- Take analgesic or anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain or discomfort, as recommended by your doctor;
- Take the antibiotic prescribed by your doctor, such as azithromycin, in a single dose on the day of surgery, as indicated by your doctor;
- Use the vaginal egg prescribed by the doctor, once a day, at night, for 10 days, starting its use 3 days after conization, or as per medical advice;
- Rest for 2 to 7 days, as per medical advice;
- Avoid light to moderate exertion on the day of surgery and the following day;
- Avoid having sexual intercourse for about 6 weeks;
- Avoid intense efforts, such as cleaning the house or going to the gym, for 30 days;
- Do not use vaginal douches or tampons, and do not take sitz baths, for at least 1 month;
- Perform intimate hygiene, 1 to 2 times a day, with the intimate soap recommended by your doctor.
During the post-operative period after conization of the uterus, it is normal for small, dark bleeds to occur, lasting around 3 to 4 weeks, which are not a sign of alarm.
However, it is recommended that women always pay attention if the bleeding is very profuse, bright red in color or if there are signs of a possible infection such as a foul smell, yellowish or greenish discharge, and fever. If these signs are present, you should go to the hospital or return to the gynecologist.
Possible complications
The main complication after conization is the risk of bleeding. Therefore, even after returning home, the woman should be alert to the appearance of profuse, bright red bleeding, as this may indicate hemorrhage.
Furthermore, the risk of infection is also quite high after conization. Therefore, women should pay attention to signs such as:
- Greenish or foul-smelling vaginal discharge;
- Pain in the lower belly region;
- Discomfort or itching in the vaginal region;
- Fever above 38ºC.
Another possible complication is the development of cervical insufficiency during pregnancy. This causes the woman’s cervix to shrink or open, causing dilation that can lead to miscarriage or premature labor. Understand better what it means to have your cervix open or closed.
Bibliography
- HEALTH LINK BC. Cone Biopsy (Conization) for Abnormal Cervical Cell Changes. Available at: <https://www.healthlinkbc.ca/health-topics/hw27835>. Accessed on June 22, 2021
- CHACON, E.; et al. SUCCOR cone study: conization before radical hysterectomy. Chacon E. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 32. 2; 117-124, 2022
- COOPER, D. B.; CARUGNO, J.; MENEFEE, G. W. IN: STATPEARLS (INTERNET). TREASURE ISLAND (FL): STATPEARLS PUBLISHING. Conization Of Cervix. 2022. Available at: <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441845/>. Accessed on January 6, 2023
- NAGAO, Y.; et al. Clinical effects of cervical conization with positive margins in cervical cancer. Sci Rep. 11. 1; 23288, 2021
- BASU, P.; et al. Management of cervical premalignant lesions. Curr Probl Cancer. 42. 2; 129-136, 2018
- MICHAAN, N.; et al. The Effect of Cervical Conization on Women’s’ Sexual Function and Psychological Health, A Prospective Observational Study. J Sex With. 19. 2; 257-262, 2022

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13