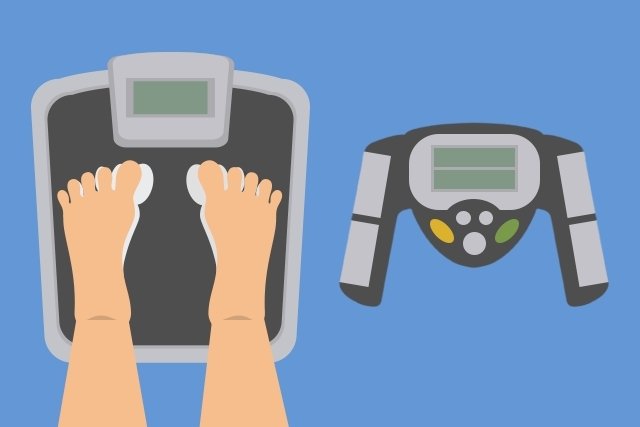
Bioimpedance is an exam that evaluates body composition, indicating the amount of water, muscle mass, fat mass and visceral fat, in addition to bone density and basal metabolic rate.
Bioimpedance is widely used by physical education professionals, doctors and nutritionists to assess whether the volume of fat and muscles is appropriate for age and gender, to check whether there is a risk of chronic diseases that can be caused by overweight and visceral fat. , in addition to helping with planning diets and training.
Bioimpedance is performed using special scales, such as Tanita, Omron or Inbody, which have metal plates that conduct a type of weak electrical current that passes through the body. Understand better what bioimpedance is in the following video:
How it is made
Bioimpedance is a test that does not cause pain, and is carried out depending on the type of scale used. On the scale that only evaluates the upper or lower region of the body, simply stand and hold the device’s sensors, or step barefoot and without socks on the metal sensors. On scales that evaluate the entire body, the person must lie face up and 4 electrodes are placed on the hands and feet.
On scales that evaluate the lower, upper limbs and trunk separately, you must climb onto the scale, over the sensors, and hold the device rod with your hands at the same time.
During bioimpedance, a light electrical current passes through the body through metal plates. This current passes easily through water and, therefore, more hydrated tissues, such as muscles, let the current pass quickly. Fat and bones have little water, making it difficult for electrical current to pass through.
Thus, the difference between the resistance of fat and bones to the electrical current, and the speed at which it passes through the muscles, allows the scale to calculate the value of the amount of lean mass, fat and water.
Make an appointment with your nearest nutritionist, using the following tool, to better understand how bioimpedance works:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
How is the preparation
To obtain the correct values, it is important to carry out preparation, including:
- Avoid eating, drinking coffee or exercising during the 4 hours before the exam;
- Drink 2 to 4 glasses of water 2 hours before the exam;
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages in the previous 24 hours;
- Do not apply cream to your feet or hands;
- Wear light and small clothes.
Preparing for bioimpedance is important because, in cases of dehydration, for example, the fat mass value may be higher than the real one. Excess body fluid can increase lean mass values, but this does not represent reality.
Types of bioimpedance balance
The main types of bioimpedance balance are:
- To the regionl: in this type of scale, the device contains only 2 electrodes and only evaluates the upper or lower region of the body;
- Total: this type of device contains 4 electrodes and evaluates the entire body, and the evaluation is generally carried out with the person lying on their back.
There is also a segmental scale, which evaluates the lower and upper limbs and the trunk separately, being considered the most accurate for performing bioimpedance.
What does the result mean
In addition to body weight and Body Mass Index (BMI), the values offered by bioimpedance devices, or scales, are:
1. Fat mass
The amount of fat mass can be given in % or in kg, depending on the type of device. Recommended fat mass values vary according to gender and age, as shown in the following table:
Ideally, the fat mass value should be in the range referred to as normal, because when it is above this value it means that there is a lot of accumulated fat, which increases the risk of various diseases, such as obesity or diabetes.
Athletes, on the other hand, normally have a lower fat percentage than normal. Understand better about the ideal body fat percentage.
2. Lean mass
The lean mass value indicates the amount of muscle and water in the body, and some scales or more modern devices already make the difference between the two values. For lean mass, the recommended values, in kg, are:
Lean mass must also be within the range of values defined as normal, however, athletes generally have higher values due to frequent training that promotes muscle building. People who are sedentary or who do not do strength exercises normally have a lower value.
Lean mass is normally used to evaluate the results of a training plan and diet, as it allows you to assess whether you are gaining muscle with the type of exercise and diet you are doing.
3. Massa muscular
The greater the amount of muscle, the greater the number of calories burned per day, which makes it easier to eliminate excess fat from the body and prevent the emergence of various diseases, such as diabetes, obesity and heart attack. This information can be given in kilos of muscle or percentage.
The amount of muscle mass only shows the weight of the muscles within the lean mass, without considering water and other body tissues. This assessment also includes the smooth muscles of some organs, such as the stomach, intestine and heart.
4. Hydration
The reference values for hydration in men and women are different and are described below:
- Woman: from 45% to 60%;
- Man: from 50% to 65%.
This value is very important to know if the body is well hydrated, which guarantees the health of the muscles, prevents cramps, ruptures and injuries, thus guaranteeing an improvement in performance and training results.
Therefore, when the value is below the reference range, it is important to increase your water intake to avoid dehydration.
5. Bone density
The bone density value must be constant over time to ensure that the bones are healthy, being a good measure to evaluate the benefits of physical activity in the elderly or people with osteopenia or osteoporosis, for example, since the regular practice of Physical exercise strengthens bones and treats loss of bone density.
6. Visceral Fat
Visceral fat tells you how much fat is stored around vital organs, such as the heart, liver and intestine. The value can vary between 1 and 59, being divided into two groups:
- Healthy: 1 a 12;
- Prejudicial: 13 a 59.
Although visceral fat is important for protecting the organs, excess of this type of fat is harmful and can cause various diseases, such as high blood pressure, diabetes and heart failure.
7. Basal metabolic rate
The basal metabolic rate is the amount of energy that the body, at rest, uses to maintain its vital functions, such as breathing, heartbeat and maintaining body temperature. This number is calculated based on the age, sex and physical activity that is entered on the scale. Learn more about basal metabolic rate.
In addition, the devices can also display metabolic age, which represents the age to which the current metabolism rate corresponds. Therefore, the metabolic age must always be equal to or lower than the current age for it to be a positive result for a healthy person.
To increase the basal metabolic rate, one must practice physical activities regularly, including high-intensity activities, such as running or swimming, and strength exercises, such as weight training and HIIT, as these activities stimulate the gain of muscle mass and accelerate breathing, stimulating energy expenditure at rest.
Furthermore, maintaining a balanced diet, prioritizing vegetables, fruits, water, proteins and healthy fats, also helps to increase the basal metabolic rate, stimulating calorie expenditure.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13