Stomatitis is a condition characterized by the appearance of wounds on the lips, tongue, gums and cheeks, similar to canker sores and ulcers, which can be single or multiple and are accompanied by other symptoms such as pain, swelling and redness.
This situation can happen as a result of blows and trauma to the mouth, which can happen due to brushing too hard, for example, or be a consequence of consuming very acidic foods, nutritional deficiencies or infection by bacteria or viruses.
Treatment for stomatitis should be guided by a general practitioner or dentist, according to the severity of the symptoms, the frequency with which they occur and the cause, and a change in eating habits, improved oral hygiene or the use of an ointment with antiviral properties may be recommended, for example. example.
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
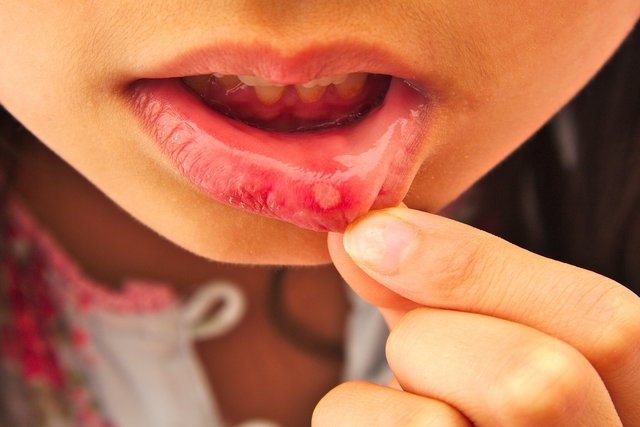
Stomatitis symptoms
The main symptom of stomatitis are lesions in the mouth, which resemble a cold sore or ulcer, and which are accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Pain in the region of the injury;
- Sensitivity in the mouth;
- Difficulty eating, swallowing and speaking;
- General malaise;
- Discomfort in the mouth;
- Inflammation around the injury;
- Fever.
Furthermore, due to pain and discomfort, it is possible that oral hygiene is not done correctly, so that it is also possible to notice bad breath and a bad taste in the mouth.
In the presence of signs and symptoms of stomatitis, it is recommended that a general practitioner or dentist be consulted, as this will allow the cause of the stomatitis to be investigated and the most appropriate treatment to be initiated.
How the diagnosis is made
The initial diagnosis of stomatitis is made by the general practitioner or dentist based on the assessment of the signs and symptoms presented by the person and the frequency with which they appear, taking into account the person’s habits and health history.
If you want to assess your risk of stomatitis, make an appointment with the general practitioner in the region closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
It may also be recommended to carry out laboratory tests to identify the cause of stomatitis, and it may be recommended to carry out microbiological analysis of the wounds, biopsy of the lesion and blood tests, such as blood count and measurement of vitamins and minerals in the blood.
Main causes
Stomatitis can occur as a consequence of several situations, the main ones being:
- Use of a toothbrush with very firm bristles;
- Brush your teeth or floss too hard;
- Use of orthodontic braces;
- Consumption of very acidic foods;
- Nutritional deficiencies, such as iron, B vitamins, vitamin C and/or folic acid;
- Chemotherapy;
- Systemic diseases, such as Behçet’s disease, inflammatory bowel disease and Kawazaki disease, for example.
Furthermore, stomatitis can occur due to infection by viruses, fungi and bacteria. If it is related to bacteria, it is common for the bacteria responsible for stomatitis to be part of the normal microbiota and have their concentration increased due to the decrease in the activity of the immune system.
In the case of viruses, the main responsible for stomatitis is the herpes virus, so this type of stomatitis is known as herpetic stomatitis, and is characterized by the appearance of a sore in the mouth, redness and bleeding in the gums. Learn more about herpetic stomatitis.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for stomatitis involves cleaning the affected area every three hours, in addition to rinsing your mouth with alcohol-free mouthwash. Eat a bland diet, with soft or cooked foods, to help reduce injuries. Understand better about the bland diet.
During crises, some natural measures such as the use of propolis extract and licorice drops can be used at the wound site, as they help to relieve burning and discomfort. Check out other natural treatments for stomatitis.
However, if the wounds are recurrent, it is recommended that a general practitioner or dentist be consulted, as in cases of herpes virus it may be necessary to use medicines such as acyclovir.
For those who suffer from food hypersensitivity, genetic factors or a weakened immune system, the general practitioner or dentist may recommend the use of triamcinolone acetonide to be applied to the lesion 3 to 5 times a day, and follow-up with the nutritionist, to that a special diet is followed, thus reducing the frequency and intensity of stomatitis attacks.
Other precautions during treatment
During the treatment of aphthous stomatitis, there are some precautions that can help with recovery, such as:
- Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth, flossing and using mouthwash several times a day;
- Rinse your mouth with warm water and salt;
- Avoid very hot foods;
- Avoid salty or acidic foods.
- Do not touch the wound or another place afterwards;
- Keep the area hydrated.
Furthermore, it is also important to drink a lot of water during treatment to maintain hydration, and it is recommended that you eat a more liquid or pasty diet, based on creams, soups, porridge and purees.
Bibliography
- BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis Literature review . 2002. Available at: <https://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0034-72992002000400019&lng=pt&tlng=pt>. Accessed on September 18, 2020
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Manual of Oral Health Specialties . 2008. Available at: <http://189.28.128.100/dab/docs/portaldab/publicacoes/manual_especialidades_bucal.pdf>. Accessed on September 18, 2020
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. What are the signs, symptoms and treatment of a patient with stomatitis? . Available at: <https://aps.bvs.br/aps/quais-os-sinais-sintomas-e-tratamento-de-um-paciente-com-estomatite/>. Accessed on September 18, 2020

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13





