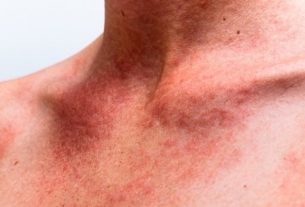
Zika virus infection during pregnancy can cause symptoms in women such as the appearance of red spots on the skin, fever above 38ºC, pain and swelling in the joints.
Furthermore, Zika virus infection during pregnancy also poses a risk to the baby. This is because this virus can be transmitted from woman to baby, causing microcephaly, a disease that can compromise the child’s neurological and physical development. Learn more about microcephaly.
The diagnosis of Zika during pregnancy must be made by a doctor, through evaluation of the symptoms and signs presented and tests that help identify the virus, such as the RT-PCR molecular test and rapid test. See how Zika is diagnosed.

Main symptoms of Zika virus during pregnancy
The main symptoms of the Zika virus in pregnancy are:
- Red spots on the skin;
- Itching on the body;
- Fever above 38 ºC;
- Headache;
- Redness in the eyes;
- Joint pain and swelling;
- Weakness.
Zika virus symptoms usually disappear after 2 to 7 days. However, even when the symptoms disappear, it is important to consult an obstetrician or infectious disease specialist so that tests can be carried out and the risk of transmitting the virus to the baby can be checked.
Possible risks for the baby
The main risk of the Zika virus during pregnancy for the baby is microcephaly. As a consequence of microcephaly, the baby may experience cognitive and visual problems, paralysis and general developmental delays. Know the signs and symptoms of microcephaly.
At what stage of pregnancy is the Zika virus dangerous?
Contaminating the baby with the Zika virus can happen at any stage of pregnancy. However, the risks to the baby are greater when the mother’s infection occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy. This is because during this period the placenta is not yet able to fully protect the baby against the Zika virus, increasing the risk of microcephaly and miscarriage.
What are the chances of a baby being born with microcephaly?
It is currently known that some women can have Zika during pregnancy and their babies do not develop microcephaly. However, the chances of the baby of mothers who have Zika being born with this condition are not yet known.
How do you know if your baby has microcephaly?
To find out if the baby has microcephaly, ultrasound is the recommended test to do during pregnancy. Furthermore, this disease can also be confirmed shortly after birth by measuring the size of the baby’s head.
How transmission happens
The main form of transmission of the Zika virus is through the bite of the Aedes aegypti mosquito. Furthermore, this virus can also be transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse or from mother to child, during pregnancy or at the time of birth.
How the diagnosis is made
The diagnosis of the Zika virus during pregnancy must be made by the doctor based on the evaluation of the signs and symptoms presented by the woman, as well as by carrying out some tests, such as the RT-PCR molecular test and the rapid test.
1. Teste molecular RT-PCR
The RT-PCR molecular test is the most used to identify Zika virus infection, as in addition to indicating the presence or absence of infection, it also informs the quantity of circulating virus, which is important for the doctor’s indication of treatment.
The RT-PCR test can identify virus particles in the blood, placenta and amniotic fluid. The result is more easily obtained when it is carried out while the woman still has symptoms of the disease.
When the result is negative, but the baby has microcephaly, it is possible that the woman had Zika for a long time and the immune system removed traces of the virus from the body or the microcephaly was caused by other factors. Know the causes of microcephaly.
2. Rapid test for Zika
The rapid test for Zika is carried out for screening purposes, as it only indicates whether or not there is infection by evaluating the antibodies circulating in the body against the virus. In case of positive results, a molecular test is recommended. In tests with negative results, the recommendation is to repeat the test and, if there are symptoms and the rapid test is negative, the molecular test is also indicated.
3. Differential examination for Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya
As Dengue, Zika and Chikungunya cause similar symptoms, one of the tests that can be carried out in the laboratory is the differential test for these diseases, which consists of specific reagents for each of the diseases and provides the result in approximately 2 hours.
What is the treatment like?
Because there are no vaccines or medications that treat Zika virus infection, treatment usually includes rest, hydration, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, or pain relievers to combat pain and fever. Find out how Zika is treated.
How to prevent Zika during pregnancy
To protect yourself from Zika during pregnancy, a woman can wear long clothing that covers most of her skin and use repellents, such as Icaridin and DEET, every day to keep mosquitoes away. See the most recommended repellents during pregnancy.
Other strategies include planting citronella or lighting citronella-scented candles because they keep mosquitoes away. Investing in the consumption of foods rich in vitamin B1 also helps keep mosquitoes away because this vitamin changes the odor of the skin, keeping mosquitoes away. Check out other strategies to avoid mosquito bites.
Furthermore, it is essential to have medical supervision throughout the pregnancy and to use a condom during sexual intercourse.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13