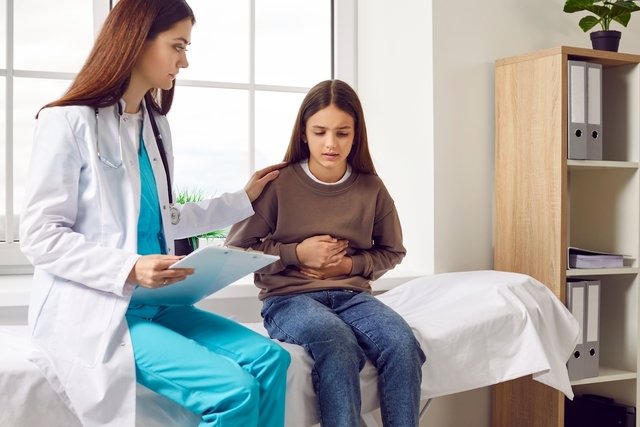
Intestinal worms are parasites that affect the wall of the intestines, such as roundworms, pinworms, tapeworms or amoeba, where they adhere to feed and reproduce, causing symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain or itching in the anus, especially at night.
These parasites can be helminths or protozoa, normally transmitted through consumption of contaminated water or food, or by walking barefoot on contaminated soil, for example.
Read too: Worms: what they are, symptoms, causes, transmission and treatment
tuasaude.com/o-que-fazer-para-prevenir-verminoses
The treatment of intestinal worms is carried out by a gastroenterologist, general practitioner or pediatrician, and involves the use of antiparasitic or deworming medications, hygiene measures or changes in diet.
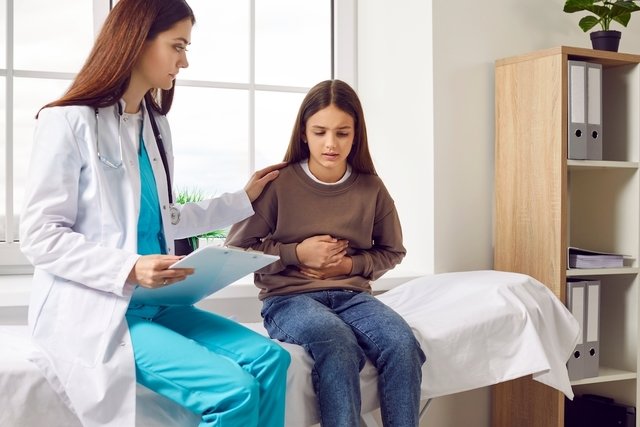

Symptoms of intestinal worms
The main symptoms of intestinal worms are:
- Frequent diarrhea, which may have blood or mucus;
- Nausea or vomiting;
- Dor abdominal;
- Swollen belly or excess gas;
- Excessive tiredness or weakness;
- Itching in the anus, especially at night;
- Vaginal discharge or itching in the vulva;
- Red spots on the skin that itch;
- Weight loss for no apparent reason;
Depending on the type of intestinal worm, the entire worm or pieces may also be seen in the feces.
Furthermore, when the worm affects other organs, such as the lungs or brain, coughing, frequent headaches or seizures may also occur. Know how to identify all the symptoms of intestinal worms.
It is important to consult a gastroenterologist, pediatrician or general practitioner whenever symptoms of intestinal worms appear, so that the type can be identified and the most appropriate treatment can be initiated.
Symptom Test
To find out if you may have intestinal worms, select what you are experiencing below:
The symptom test is only a guidance tool and does not serve as a diagnosis or replace consultation with a gastroenterologist, pediatrician or general practitioner.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of intestinal worms is made by a gastroenterologist, pediatrician or general practitioner through evaluation of symptoms, health and travel history.
Make an appointment with the gastroenterologist in the region closest to you:
Taking care of your health has never been easier!
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must request a complete blood count, which usually shows high eosinophils, and a parasitological stool test, to identify the type of worm. See how the parasitological fecal examination is carried out.
Other tests that the doctor may order are X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography, to assess the presence of the worm in the brain or lungs, for example.
Read too: How to confirm if I have intestinal worms: examination and symptom test
How transmission happens
The main ways of transmitting intestinal worms are:
- Consumption of contaminated water or food;
- Poor hygiene of vegetables or fruits;
- Holding dirty hands in your mouth;
- Consume raw foods, such as fish, meat or chicken;
- Living or traveling to regions that do not have adequate basic sanitation;
- Walking barefoot on sand, dirt or mud.
These forms of transmission may vary depending on the type of parasite.
Generally, the risk of intestinal worms is greater in children, the elderly, people with a weakened immune system or those who have HIV infection or AIDS.
Read too: Worms in Children: 8 Symptoms, Treatment and Care
Types of intestinal worms
The main types of intestinal worms are:
1. Oxyurus
Pinworm is a helminth of the species Enterobius vermicularis, being the most common type of intestinal worm that mainly affects children, causing intense itching in the anus, especially at night. See other pinworm symptoms.
This type of worm is transmitted through the consumption of food contaminated with eggs of this parasite or by putting a dirty hand in the mouth, for example.
2. Ascaridia
Ascariasis, also known as roundworm, is caused by the helminth Ascaris lumbricoides which can be transmitted through the consumption of water or food contaminated with eggs of this parasite.
This type of intestinal worm can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain or discomfort, diarrhea or constipation, or the presence of the worm in the stool. Learn how to identify the symptoms of ascariasis.
3. Taeniasis
Taeniasis, also known as solitary, is a flatworm that can be transmitted through ingestion of raw or undercooked beef or pork contaminated with taeniasis larvae. Tape soles e Taenia saginata. Understand how taeniasis is transmitted.
The worm caused by this parasite may not cause symptoms or cause anal itching or the presence of pieces of the worm in the feces.
4. Schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis is a type of helminth of the species Schistosoma mansoni which can be transmitted through penetration of the skin by cercariae present in contaminated water, especially in places where there are large numbers of snails.
This type of worm can cause symptoms such as redness and itching of the skin where the parasite enters, swelling of the belly, also called water belly, or the presence of blood in the stool. Learn more about the transmission and symptoms of schistosomiasis.
5. Hookworm
Hookworm, also known as yellowing, is caused by helminths Ancylostoma duodenale or American killer.
This type of intestinal worm can be transmitted by walking barefoot on soil contaminated with larvae of these parasites, causing symptoms such as yellowed skin, fever, desire to eat dirt or dark, foul-smelling feces. Check out other symptoms of hookworm.
6. Giardiasis
Giardiasis is caused by the protozoa Giardia lamblia transmitted through ingestion of cysts present in contaminated water, food or objects.
This type of worm is more common in children, causing symptoms such as yellowish stools that float in the toilet, diarrhea or abdominal pain. See how to identify the symptoms of giardiasis.
7. Amebiasis
Amebiasis is caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica which is transmitted mainly through the ingestion of cysts present in water or food contaminated with feces. Understand better how amoebiasis is transmitted.
This type of parasitism may cause no symptoms, or lead to the development of abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, nausea, nausea, excessive tiredness and the presence of blood or secretion in the stool.
Read too: 7 Diseases caused by protozoa: symptoms and treatment
8. Trichuriasis
Trichuriasis is a type of intestinal worm caused by the helminth Trichuris trichiuratransmitted by consumption of water or food contaminated by feces containing eggs of this parasite.
Trichuriasis causes symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and weight loss. See other symptoms of trichuriasis.
9. Strongyloidiasis
Strongyloidiasis is caused by intestinal helminth Strongyloides stercoralistransmitted by skin contact with soil contaminated with the larvae of this worm.
This type of intestinal worm can cause symptoms such as red spots on the skin where the larvae penetrate, diarrhea, abdominal gas or a dry cough. Know how to identify the symptoms of strongyloidiasis.
How the treatment is carried out
Treatment for intestinal worms must be carried out under the guidance of a gastroenterologist, pediatrician or general practitioner, with the aim of eliminating the parasite and relieving symptoms.
The main treatments for intestinal worms are:
1. Use of medicines
The use of antiparasitic or deworming medications is one of the main treatments for intestinal worms and should be used with a doctor’s advice according to the type of parasite.
Thus, medications may be prescribed by the doctor, such as albendazole, mebendazole, nitazoxanide or secnidazole, for example. See the main remedies for worms.
It is recommended that the whole family undergo treatment with medicines recommended by the doctor, even if there are no apparent symptoms, as this makes it possible to prevent contagion.
2. Diet for intestinal worms
The intestinal worm diet aims to improve nutritional deficiencies, strengthen the immune system and help alleviate symptoms, such as diarrhea, for example.
Therefore, the diet should include probiotic foods, such as yogurt, kefir or kombucha, for example, in addition to avoiding foods rich in sugar or fat, for example. Check out the main probiotic foods.
These foods should be consumed with the guidance of a nutritionist, to complement treatment with medications recommended by the doctor.
3. Hygiene measures
During treatment for intestinal worms, it is important to wash your hands thoroughly before and after going to the bathroom or preparing food, to avoid transmitting the worm to other people in the house.
In addition, it is recommended to change sheets, blankets, underwear, towels and pajamas daily and wash in hot water.
Fruits and vegetables must also be properly cleaned, in addition to avoiding eating raw or undercooked foods to avoid recontamination. Learn how to clean food correctly.
Natural Treatment Options
Some natural treatment options for intestinal worms, such as drinking turmeric tea or mastruz tea, can help fight worms. Learn how to prepare home remedies for worms.
However, these home remedies should not replace the use of medicines prescribed by a doctor, but can be used to complement medical treatment.
Watch the following video with tips on other home remedies for intestinal worms:
How to prevent intestinal worms
To prevent intestinal worms it is recommended:
- Wash your hands thoroughly after using the bathroom or changing children’s or babies’ diapers;
- Wash your hands with water and neutral soap, cleaning well under your nails, before cooking;
- Properly clean fruits, vegetables and legumes;
- Cook food well, avoiding eating raw or undercooked food;
- Avoid biting nails;
- Avoid walking barefoot, especially on dirt and mud;
- Do not drink water that is not properly filtered or boiled.
In addition, water suitable for human consumption must be consumed, which can be filtered or boiled, and which must also be used to wash containers. Learn how to make water safe to drink.
Possible complications
Intestinal worms can cause complications such as malnutrition due to poor absorption of nutrients by the intestines or anemia.
In addition, intestinal obstruction may also occur due to the presence of large quantities of worms in the intestine, which must be treated immediately in the hospital. Know how to identify the symptoms of intestinal obstruction.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13