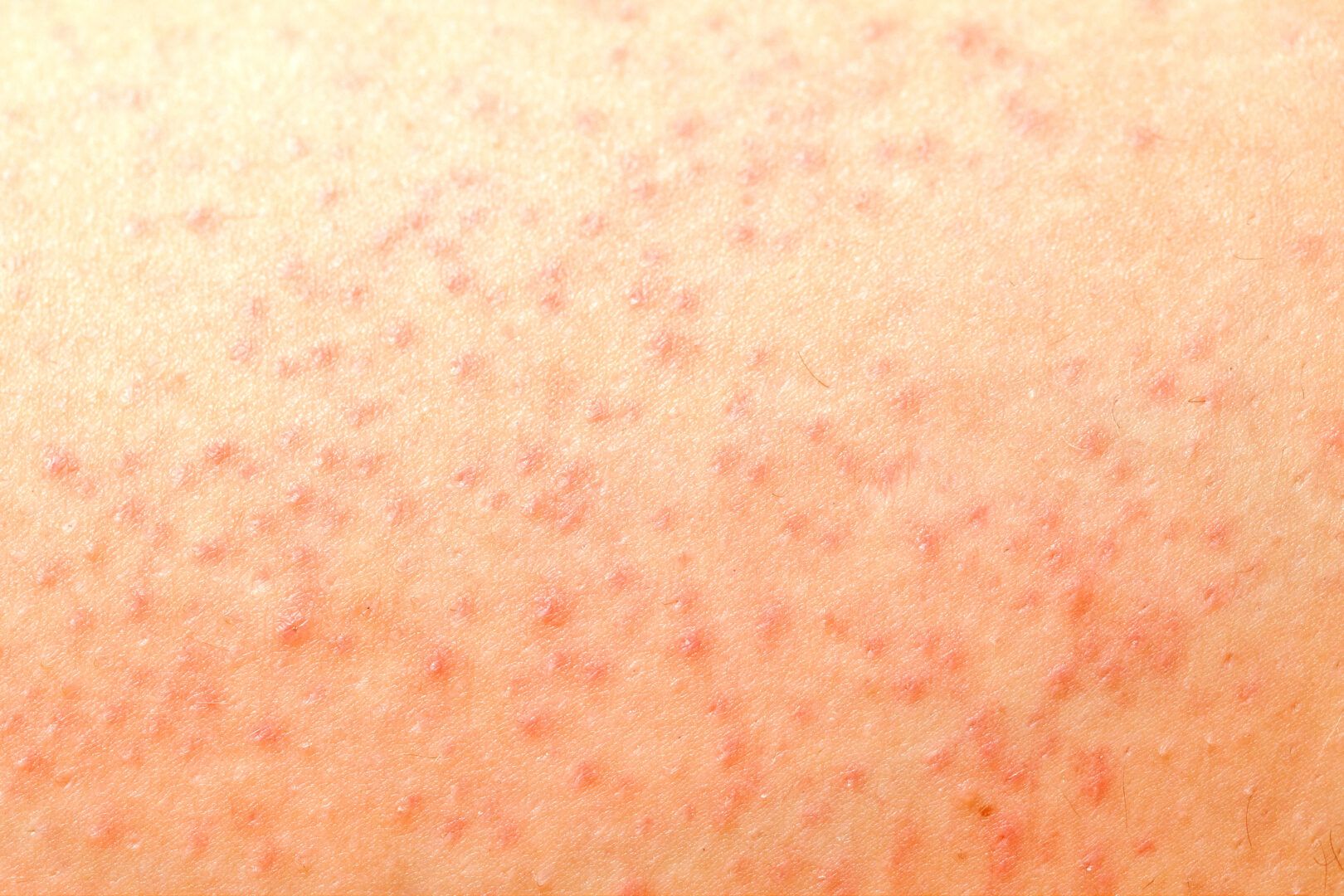
Folliculitis is a skin problem that can manifest itself in different ways. Despite its simple treatment, it requires a lot of attention.
Folliculitis, a dermatological problem with a high incidence, is an infection of the hair follicles. They are small structures that produce and house hair on the human body. It is caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses or other infectious agents.
The main symptoms of folliculitis are:
- Small red or pus-filled balls at the roots of the hair;
- Itching, pain and sensitivity in the skin;
- Redness and swelling in the affected region.
7 facts about folliculitis that are important to know
Folliculitis is a problem that can affect us at any time and it is very important to keep in mind that:
1. It can occur in almost every part of the body
Hair follicles are present on most of the skin’s surface, except on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and mucous membranes.
We call it folliculitis inflammation of these follicles. It can occur on any part of the body that has hair, but is more common in areas that suffer friction from clothing or waxing, such as the face, neck, armpits, legs and intimate area.
Folliculitis is usually a mild, self-limiting conditionwhich resolves in a few days with hygiene measures and local care.
However, in some cases, it can become chronic or complicated, leading to the formation of abscesses, scars or spots on the skin. In these cases, It is recommended that you consult a dermatologist to assess the cause. and adequate treatment of folliculitis
2. It has different causes
The main cause of folliculitis is bacterial infection, usually staphylococci, which penetrate the follicles through small lesions in the skin.
However, other possible causes are:
- Chemical or physical irritation;
- Obstruction of pores;
- Hormonal change;
- Ingrown hairs;
- Topical application of corticosteroids;
- Jacuzzis or public swimming pools with unregulated chlorine and pH levels;
- Wounds or cuts;
- Overweight;
- Immunosuppression;
- Waxing.
See too: Scalp folliculitis – What it is, types and treatments
3. There are people who are more prone to folliculitis
Some people are more likely to develop folliculitis than others, due to factors such as:
- Having oily or acne-prone skin, which favors the accumulation of sebum and dirt in the pores.
- Wear tight or synthetic clothing, which prevents the skin from breathing and causes friction and irritation.
- Shave, wax or cut your hair frequently, especially in sensitive areas such as the bikini line or armpits.
- Sweating excessively or being exposed to humid and hot environments, which facilitate the proliferation of microorganisms on the skin.
- Having diabetes, obesity, low immunity or other conditions that affect the body’s resistance to infections.
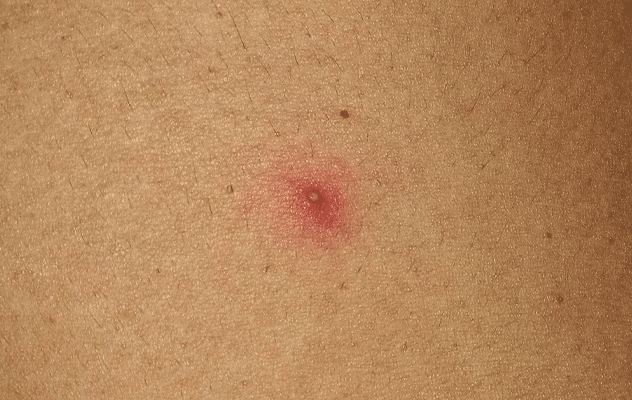
4. A boil is a type of folliculitis
A boil is a bacterial infection which affects a hair follicle and the tissue around it. It forms when a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus enters the follicle through a skin injury, such as a cut or insect bite. The bacteria causes inflammation in the follicle, which manifests as “simple” folliculitis, i.e. a small, red, painful pimple on the surface of the skin.
Left untreated, it can spread to the deeper layers of the skin and form a boil, i.e. a pus-filled abscess that rises above the skin and can be several centimeters in diameter.
The boil causes a lot of pain, heat, redness and swelling in the affected area. As it matures, it may spontaneously drain pus or require medical intervention to be opened and cleaned.
5. There are other types of folliculitis
Based on its severity, folliculitis can be classified as superficial or deep, as follows:
I – Types of Superficial folliculitis:
1. Staphylococcal folliculitis: It is the most common and is caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, or simply staphylococci, which usually lives in harmony on our skin, but after an injury when shaving or waxing, for example, can trigger inflammation in the follicles. It manifests as small pustules or inflamed nodules around hair follicles.
2. Pseudomonas folliculitis: Caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, which can be found in whirlpools, jacuzzis and swimming pools that have unregulated chlorine and pH levels, due to the use of contaminated objects, prolonged treatment with antibiotics, waxing or hospital exposure. Like staphylococcal folliculitis, it manifests itself as small pustules or inflamed nodules around hair follicles, but it tends to be more resistant to treatment and can cause more serious complications.
3. Pityrosporic or Malassezia folliculitis: Malassezia is a genus of fungus that, despite normally living on our skin without creating problems, under certain circumstances can cause dandruff and Pityriasis versicolor, an infectious and non-contagious skin disease. It appears in situations of excessive sweating, increased sebum production, prolonged treatments with antibiotics or corticosteroids, affecting mainly the back, shoulders and chest, being more common in adolescents and young adults.
II – Types of deep folliculitis
1. Beard sycose: It is a fungal infection of the hair follicles on the face and neck, caused by a bacterial infection. Symptoms include papules, pustules, nodules and scabs in the beard area, which may be itchy or painful. Diagnosis is made by direct examination, culture or biopsy of the lesions. Treatment consists of oral antifungals, under medical prescription.
2. Gram-negative folliculitis: This disease often affects people with acne or rosacea who have taken oral antibiotics for a long time, which disrupts the skin’s normal flora and encourages the growth of these microorganisms.
3. Boils and carbuncles: are bacterial skin infections that cause inflammation and pus in hair follicles. A boil is a single, painful lesion that can rupture and drain. An anthrax is a group of boils, connected to each other, and forming a larger area of infection. Treatment depends on the severity and may include antibiotics, surgical drainage, or warm compresses.
6. Treatment depends on the cause
Treating folliculitis will depend on the cause and severity of the infection, but, in most cases, it is effective and without consequences. Then, treatment may include hygiene measures, use of antibiotics or antifungal creams, ointments or tablets, or surgical drainage of boils. Therefore, the most important thing is to see a dermatologist to assess the cause and appropriate treatment.
7. Prevention is simple
To prevent folliculitis, it is important:
- Keep skin clean and dry,
- Use gentle skin cleansing products,
- Wash after physical exercise,
- Avoid using irritating or comedogenic products – those that clog pores,
- If there are lesions on the skin, it is important not to scratch and clean the affected area with antibacterial soap and cold water,
- Laser hair removal can be a good resource to avoid folliculitis,
- Choose comfortable, cotton clothes,
- Follow the guidance of a dermatologist on the most appropriate methods of hair removal.
So, what did you think of this article? If you’re interested, check out groin folliculitis, what is it? Causes, treatment and prevention
Sources: Tua Saúde, Dráuzio Varella, Minha Vida, Derma Club, Elsevier, Saber Vivir TV, Saúde e Bem Estar, Mayo Clinic

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13