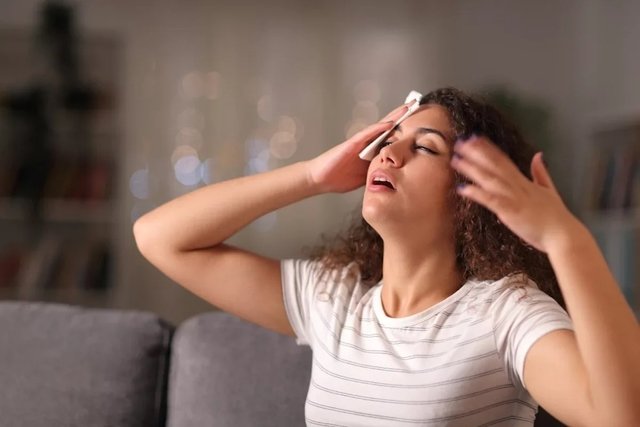
Cold sweat is a response from the body with the aim of protecting the body in dangerous situations or in cases where there is a decrease in the amount of oxygen circulating in the blood, cold sweat may be noticed in cases of hypoglycemia, hypotension, anxiety, hypoxia, generalized infection and shock.
Cold sweat does not normally occur on the body, being localized. In other words, it can appear on the palms of the hands, in the armpits and on the soles of the feet, happening suddenly.
Although sweat disappears naturally, if it is frequent, it is important that the general practitioner is consulted to check whether there is any condition that leads to cold sweat and, therefore, the most appropriate treatment can be initiated.
The main causes of cold sweat are:
1. Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia generally occurs when blood sugar levels drop below 70 mg/dl, causing symptoms such as cold sweats, headache, fainting, blurred vision, mental confusion, weakness, malaise, nausea or drowsiness. See more symptoms that may occur during hypoglycemia.
To find out your blood glucose values, you can take a quick test with a handheld device, called a glucometer, or go to the health center to have the measurement taken, which is most of the time free.
What to do: At the first symptoms of hypoglycemia, the person should sit down as soon as possible and eat foods rich in sugar or easily digestible carbohydrates, such as fruit juice, candy or cake. If the symptoms persist, or the person faints, put some sugar under the tongue and go to the emergency room for medical help.
2. Low blood pressure
When arterial hypotension occurs, better known as low blood pressure, there may be a decrease in oxygen reaching the brain and some organs, which may not only cause cold sweats, but also dizziness, palpitations, weakness, blurred vision, malaise, paleness or fainting. .
What to do: During a hypotension crisis, the person should try to elevate their legs so that they are above the trunk and drink fluids. Find out what you can do to avoid having low blood pressure.
3. Stress and anxiety
In situations of stress and anxiety, the body reacts by producing cold sweats, mainly on the forehead, hands, feet and armpits. In addition to these symptoms, a person suffering from anxiety may also feel muscle tension, malaise, nausea, vomiting, palpitations and tremors. See other symptoms you may have in anxiety situations.
What to do: There are some ways that can help control anxiety, such as receiving a relaxing massage or taking a warm bath, taking natural remedies such as chamomile tea or passion fruit juice. In more serious cases where it is difficult to control anxiety, psychological support or even medications that can be prescribed by a doctor may be necessary.
It is also important that in cases where the symptoms of the anxiety attack are intense, the person is referred to the hospital so that the possibility of a heart attack can be ruled out.
4. Decrease in oxygen
In cases of hypoxia, which is the reduction in the supply of oxygen to the body’s tissues, symptoms such as cold sweats, shortness of breath, weakness, mental confusion, dizziness and in more serious cases fainting and coma can occur which can lead to death, for example. This means you should go to the emergency room urgently as soon as the first symptoms appear.
Decrease in oxygen can occur in situations where blood circulation is poor, in cases of intoxication, when in places with altitudes above 3000 meters, in people with lung diseases or anemia.
What to do: the Treatment consists of using an oxygen mask to normalize blood levels and resolving the cause of hypoxia with specific treatments such as nebulization for asthma, medications to improve the functioning of the lungs or heart, treatments for anemia or antidotes for poisoning, for example . In severe cases, the use of artificial respiration may be necessary.
5. Generalized infection
Generalized infection or sepsis consists of an infection caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi that affects various organs of the body, which can lead to their failure and hinder oxygenation, which can cause cold sweats, high fever, tremors, a drop in blood pressure or tachycardia.
What to do: Treatment for generalized infection consists of taking antibiotics, analgesics and anti-inflammatories and replacing fluids. However, these measures may not be sufficient and artificial respiration may be necessary in an intensive care unit.
6. Shock
During a state of shock, which can occur due to a major trauma, blow, allergic reaction or an accident, a drop in oxygen can occur, preventing the organs from receiving the sufficient amount they need to function, which can cause symptoms such as cold sweats, paleness , increased pulse rate, nausea and vomiting, weakness, dizziness or anxiety.
What to do: The person who goes into a state of shock may or may not be conscious, but in all cases it is advisable to seek medical help immediately, call an ambulance or take the person to the emergency department so that they receive the fastest possible treatment.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13