Skin cancer occurs due to the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of the different types of cells that make up the layers of the skin, and can be divided into some categories according to the characteristics of the changes, such as non-melanoma skin cancer, melanoma and skin sarcomas.
In general, non-melanoma skin cancers are easier to treat and have a greater chance of being cured, while melanomas are more difficult to treat, especially when identified at a more advanced stage.
When a suspicious mole appears on the skin, which changes color, shape or increases in size, you should consult a dermatologist to check whether there is malignancy and what to do in each case.
Types of skin cancer
Skin cancer can be classified into:
1. Basal cell carcinoma
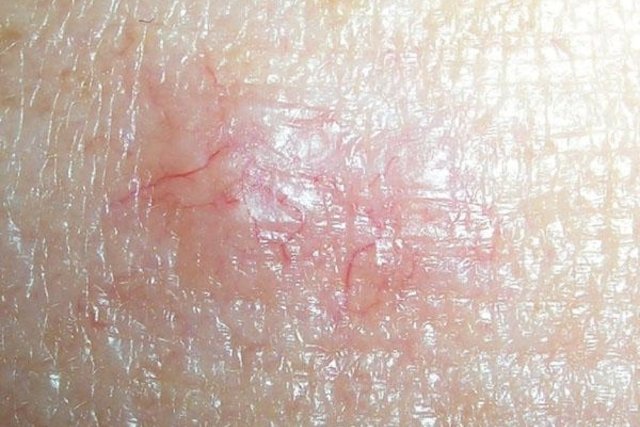
Basal cell carcinoma is the least serious and most common type of non-melanoma cancer, corresponding to more than 95% of cases, and appears in basal cells located in the deepest layer of the skin, appearing as a bright pink spot on the skin that It grows slowly, may present a crust in the center of the spot and may bleed easily. This type of cancer is more common in people with fair skin, after the age of 40, due to lifelong sun exposure.
Where it can appear: It almost always appears in areas with a lot of sun exposure, such as the face, neck, ears or scalp, but it can also appear in other parts of the body.
What to do: In case of suspicion, a dermatologist should be consulted to evaluate the spot on the skin and begin appropriate treatment, which, in these cases, involves minor surgery or laser application to remove the spot and eliminate all affected cells. Understand more about this type of cancer and its treatment.
2. Squamous cell carcinoma
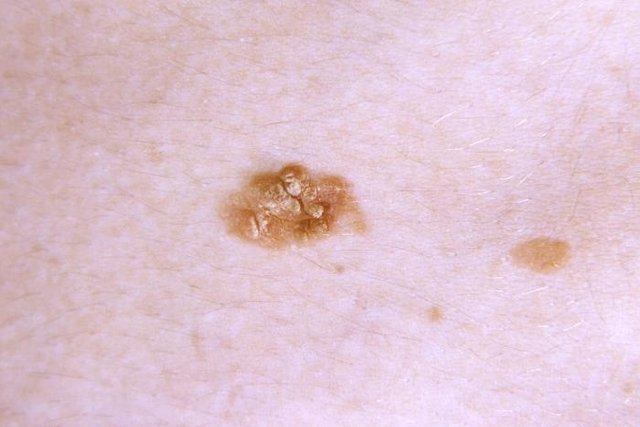
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of non-melanoma skin cancer and appears in squamous cells located in the most superficial layers of the skin. This type of cancer is more common in men, although it can also develop in women of any age, especially in people with light skin, eyes and hair as they have less melanin, which is the skin pigment that protects against ultraviolet radiation.
This type of cancer appears in the form of a red lump on the skin or a bruise that peels and forms a scab, or looks like a wart.
Sun exposure is the main factor that causes squamous cell carcinoma, but it can also happen in those who undergo chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments or have chronic skin problems, such as wounds that do not heal. Generally, people who are diagnosed with an actinic keratosis patch, and who do not take the treatment recommended by their doctor, also have a high chance of developing this type of skin cancer.
Where it can appear: It can appear on any part of the body but is more common in areas exposed to the sun, such as the scalp, hands, ears, lips or neck, which show signs of sun damage such as loss of elasticity, wrinkling or change in skin color.
What to do: As with other types, it is important to consult a dermatologist to confirm the type of spot and begin treatment, which, in these cases, is initially done with minor surgery or another technique, such as applying cold, to remove the majority of altered cells. After that, if necessary, radiotherapy can also be performed, for example, to remove the remaining cells.
3. Merkel’s carcinoma
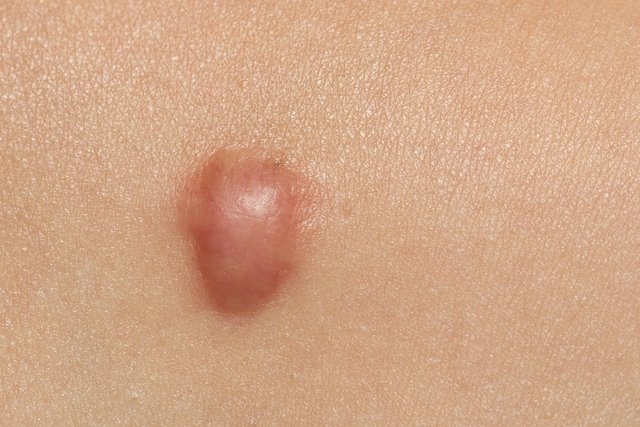
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rarer type of non-melanoma cancer and is more common in older people due to prolonged exposure to the sun throughout life or people with a weaker immune system.
This type of cancer usually appears as a painless skin-colored or bluish-red lump on the face, head or neck and tends to grow and spread quickly to other parts of the body.
Where it can appear: It can appear on the face, head or neck, but it can also develop on any part of the body, even in areas not exposed to sunlight.
What to do: You should consult a dermatologist if a spot, freckle or lump appears that changes size, shape or color, grows quickly or bleeds easily after minor trauma, such as washing the skin or shaving, for example. The dermatologist must evaluate the skin and initiate appropriate treatment which, in these cases, can be done with surgery, radiotherapy, immunotherapy or chemotherapy.
4. Malignant melanoma
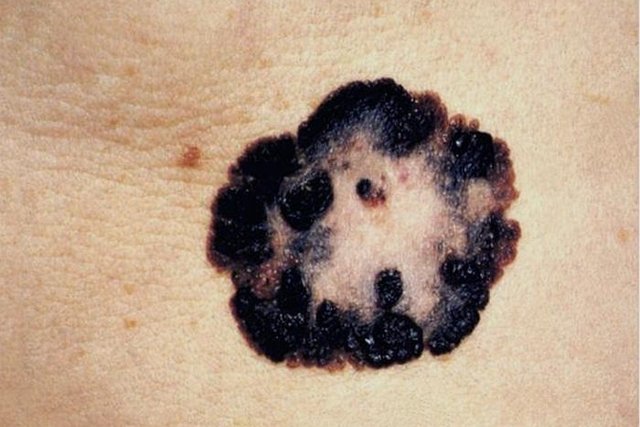
Malignant melanoma is the most dangerous type of cancer of all and normally appears as a dark spot that becomes deformed over time. It can be fatal if not identified early, as it can develop quickly and affect other organs such as the lungs. See how to evaluate a skin spot to find out if it could be melanoma.
Where it can appear: It often develops on sun-exposed areas such as the face, shoulders, scalp or ears, especially in people with very fair skin.
What to do: Since this type of cancer has a greater chance of being cured when treatment is started at an early stage, it is important that dark spots that grow over time and have an irregular shape are quickly evaluated by a dermatologist. In most cases, treatment begins with surgery to remove most of the cells and, after that, it is usually necessary to undergo radiotherapy or chemotherapy to eliminate any cells that remain in the skin.
5. Skin sarcomas
Sensitive content
This image may contain content that is uncomfortable for some people.
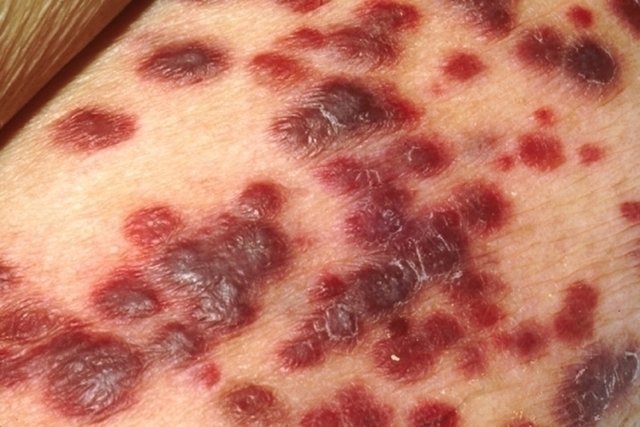
Skin sarcomas, such as Kaposi’s sarcoma or dermatofibrosarcoma, are a type of malignant skin cancer that affects the deeper layers of the skin.
Dermatofibrosarcoma can appear spontaneously after trauma, in surgery or burn scars, due to herpes virus type 8 (HHV8) infection or genetic changes. It is generally more common in young men, but can also occur in women at any age and appears as a red or purple spot on the skin and may resemble a pimple, scar or birthmark, especially in the trunk of the body. In more advanced stages, wounds may form at the site of the tumor, bleeding or necrosis of the affected skin.
Kaposi’s sarcoma is more common in people with a weakened immune system, such as people who have had some type of transplant or who have HIV infection or herpes virus type 8. This type of tumor appears as purplish-red spots on the skin and can affect the entire body. Learn more about Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Where it can appear: most common to appear on the trunk, head, neck, legs, arms and in rare cases in the genital region.
What to do: You should consult a dermatologist if a red spot appears on the skin for a more appropriate diagnosis. This type of tumor is aggressive, can spread to other parts of the body and must be treated with surgery, radiotherapy or molecular therapy. In addition, people with HIV infection must undergo frequent medical monitoring and take medications to control the infection.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13