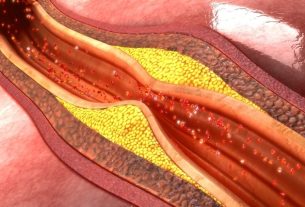
Treatment for atherosclerosis must be indicated by a cardiologist and aims to reduce the fatty plaques that are present inside the vessels and heal the lesions that remain in the area, favoring blood circulation. To do this, the doctor may recommend changing your lifestyle, taking medication or performing surgery.
Atherosclerosis is the accumulation of fat in the artery walls, forming fatty plaques or atheroma plaques, which make it difficult for blood to pass through the vessel. It is often associated with increased “bad” LDL cholesterol and low levels of HDL, called “good” cholesterol. Learn more about atherosclerosis.
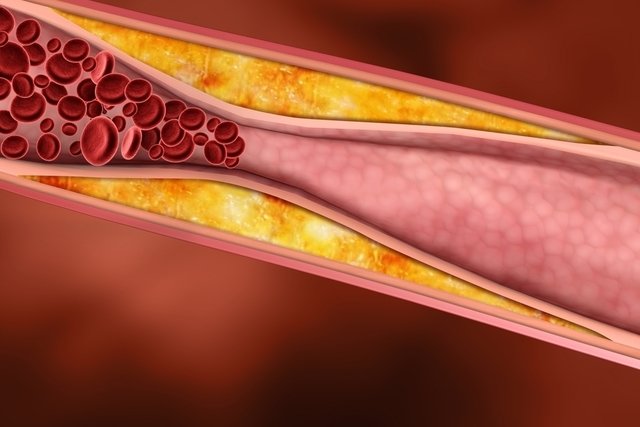
1. Lifestyle changes
Most of the time, treatment for atherosclerosis consists of changing your lifestyle, because healthy habits help reduce the risk of developing other heart diseases.
Therefore, it is recommended to practice physical activity regularly, as in addition to contributing to weight loss, it also prevents the accumulation of fat in the arteries, promotes the formation of healthy blood vessels and improves blood circulation.
It is also important to have a healthy and balanced diet, giving preference to fruits, vegetables, fish, cereals and olive oil, as they are rich in fiber and good fats that prevent the accumulation of fat inside the cases. One diet option to help treat atherosclerosis is the Mediterranean diet, which is based on the intake of natural foods and fewer processed products.
2. Use of medicines
Medicines for atherosclerosis must be recommended by a cardiologist after evaluating the person’s exams, health status and lifestyle. Some examples of remedies for atherosclerosis are:
- Inhibitors angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE): work to lower blood pressure and protect the heart and kidneys;
- Antiplatelets: better known as aspirin, they serve to prevent the formation of clots in the arteries;
- Beta blockers: reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure;
- Calcium channel blockers: relax the arteries, lower blood pressure and reduce tension on the heart;
- Diuretics: they act by lowering pressure, eliminating water from the body, they also serve to treat heart failure;
- Nitrates: relieve chest pain and improve blood flow to the heart;
- Statins: help reduce cholesterol.
It is important to follow the cardiologist’s instructions regarding the use of these medications, such as the correct dose and correct times. Furthermore, along with the use of medication, it is necessary to change your lifestyle and diet, as this is how you can avoid the consequences of atherosclerosis.
3. Surgery
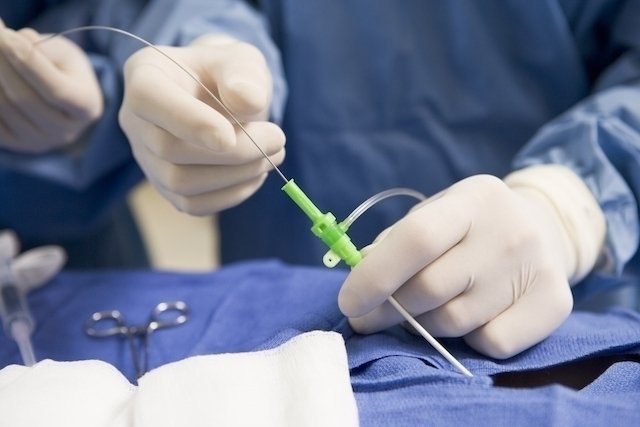
Often, when medications are no longer able to reduce the fatty plaques on the artery walls, surgery is necessary to remove this fat. The types of surgeries to treat atherosclerosis depend on the technique used, as well as the severity of the disease. Angioplasty or placement of stent is a type of surgery performed in these cases, in which the doctor places a tube, called a stentin the obstructed part, to open the artery and facilitate the passage of blood.
Another surgery recommended for atherosclerosis is a saphenous bypass, which is when the doctor replaces a clogged artery in the heart with another artery in the leg. Catheterization can also be performed, which is the introduction of a tube, the catheter, to unblock an artery in the heart. See more details about how cardiac catheterization is performed.
4. Natural treatment
There are some natural products available to combat atherosclerosis, and most of these substances help reduce cholesterol and consequently reduce atheroma plaques in the arteries, facilitating blood circulation. Among them are:
- Monaco Q: found in red yeast rice, which is a traditional ingredient in Chinese medicine and helps lower blood cholesterol;
- Sterols or stanols: present in vegetable oils such as nuts, fruits, seeds and grains and help prevent the intestine from absorbing fat;
- Soluble fibers: contains substances called beta glucans, present in oat bran, which help reduce cholesterol by eliminating fat in feces;
- Allicin: it is a substance found in garlic and has an anti-inflammatory action that delays the formation of atheroma plaque;
- Niacin: it is also known as vitamin B3, present in foods such as liver, chicken, salmon and helps control cholesterol;
- Curcumin: present in saffron, it works by reducing fatty plaque on the artery wall;
- Omega 3: present in foods such as fish, it helps reduce blood fat levels and is capable of regulating blood pressure and clotting;
These substances are found in foods, but may be available in capsules for dietary supplementation. However, it is important to always follow medical advice and respect the recommendations of the professional herbalist for using these capsules.
There are other foods and products that help in the treatment of atherosclerosis, facilitating blood circulation and preventing obstruction of blood vessels, such as buckwheat, red vine, centella asiatica and horse chestnut.
Signs of improvement
Treatments for atherosclerosis are based on the use of medication and changes in lifestyle habits and when carried out they help to reduce fatigue, increasing physical stamina, reducing stress and helping to lose weight.
Signs of worsening
Atherosclerosis often has no symptoms, but in cases where fat completely blocks an artery, some signs may appear. These signs will depend on the location of the artery that the fat is obstructing and the disease caused by this complication. If the blood flow is interrupted in any artery of the heart, an acute myocardial infarction may occur and signs such as pain and pressure in the chest on the left side, numbness or tingling in the left arm and discomfort may appear. Learn more about heart attack symptoms.
However, if an artery in the brain is compromised, signs such as difficulty speaking, crooked mouth or difficulty seeing may appear. In these cases, it is necessary to quickly go to the hospital or seek medical attention from a cardiologist.
Bibliography
- Moss, Joe; RAMJI, Deepak. Nutraceutical therapies for atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol. 13. 513-532, 2017
- RACHEL, David. Integrative Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2018. 522.
- HEALTHLINE. Atherosclerosis. Available at: <https://www.healthline.com/health/atherosclerosis#treatment>. Accessed on October 4, 2019
- Faludi AA, et al. Update of the Brazilian guideline on dyslipidemia and prevention of atherosclerosis. Brazilian Society of Cardiology. 109. 2; 18-21, 2017

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13