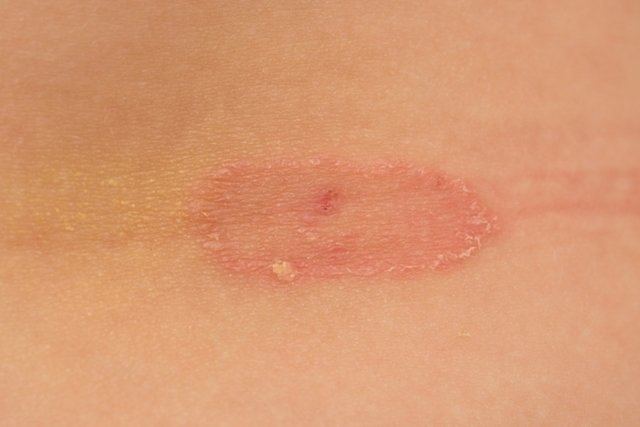
There are several diseases that fungi can cause in people, which can be mycoses of the skin, nails, mucous membranes or scalp, such as white cloth, ringworm, chilblains, thrush or candidiasis, for example.
Generally, fungi coexist harmoniously with the body, but they can cause diseases when they manage to circumvent the body’s protective barriers, which occurs mainly during periods of reduced immunity or skin injuries.
Furthermore, although fungal infections are most often superficial and easily treated, there are species of fungi that can cause deep lesions and even reach the blood circulation and organs such as the lungs, as is the case with sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis or aspergillosis. , for example.

Main diseases caused by fungi
Although there are numerous diseases caused by fungi, some of the main ones are:
1. White cloth
Also known as beach mycosis, this infection has the scientific name of Ptiriasis versicolor, and is caused by the fungus Malassezia furfur, which causes rounded spots on the skin. Generally, the spots are white in color, as the fungus prevents the production of melanin when the skin is exposed to the sun, and are most common on the trunk, abdomen, face, neck or arms.
How to deal with: Treatment is usually carried out with creams or lotions based on antifungals, such as Clotrimazole or Miconazole, recommended by the dermatologist. In the case of very large lesions, the use of tablets, such as Fluconazole, may be indicated. Understand better what white cloth is and how to treat it.
Don’t ignore the signs your body is giving you!
2. Had
Scientifically called dermatophytosis, this fungal infection is also known as tinea, and can affect different parts of the body, such as skin, hair and nails, and is caused by fungi such as Trichophyton, Microsporum or Epidermophytonwhich are transmitted from one person to another through contact, or also through contaminated soil and animals.
Some of the main injuries caused are:
- Had corporealalso called impingement and appears on any area of the skin;
- There were feetalso called chilblains or athlete’s foot, which is located between the toes;
- Had cruriswhich develops in the groin;
- It had capitalsor the scalp, which is more common in children and can cause hair loss there;
- Tie of the nailswhich makes the nail thick and dull.
The lesion that appears on ringworm is usually scaly, red and very itchy. Generally, without adequate treatment, the lesion spreads little by little and is very contagious.
How to deal with: Treatment is done with antifungal ointments, such as Miconazole, Clotrimazole or Itraconazole, and can last weeks to months. When there is a serious infection, or when the nails are very affected, it may be necessary to use tablet medications, such as Fluconazole, Itraconazole or Terbinafine. During treatment, it is essential to dry your feet well after bathing and avoid closed shoes for a long time.
Learn more about dermatophytosis.
3. Candidiasis
There are several species of fungi that are part of the family Candidathe most common being Candida albicans which despite naturally inhabiting the body, especially the mucosa of the mouth and intimate region, can cause different types of infection in the body, especially when immune defenses are impaired.
The most affected areas of the body are skin folds, such as the groin, armpits and between the fingers and toes, the nails, and it can also affect mucous membranes, such as the mouth, esophagus, vagina, penis and rectum. Furthermore, the infection can be serious enough to spread through the bloodstream and reach organs such as the lungs, heart or kidneys, for example. Discover the main skin mycoses.
How to deal with: Treatment for candidiasis is mainly done with antifungal ointments such as fluconazole, clotrimazole, nystatin or ketoconazole. However, in more serious cases or infections in the blood and body organs, it may be necessary to use antifungals in pill form or through a vein. Find out more about how candidiasis is treated.
4. Sporotrichosis
This mycosis can go beyond the skin and also affect the subcutaneous region and lymph nodes. This infection is caused by fungi from the family Sporothrix spp., which inhabit nature and are present in the soil, plants, leaves and wood, for example, therefore, they mainly infect farmers, gardeners or farmers.
This fungus can also be transmitted by scratches from infected cats. Generally, skin infection causes the appearance of a painless, reddish lump that grows gradually. In some cases, especially in people with compromised immunity, various lesions may appear, as well as spread through the bloodstream and infect lungs, bones, joints, testicles and even the brain.
How to deal with: Treatment is with oral or intravenous antifungals, such as Itraconazole, for 3 to 6 months, and in more severe cases it may be necessary to use intravenous antifungals, such as Amphotericin B, which may last for 12 months.
5. Aspergilose
It is the infection caused by the fungus Aspergillus fumigatuswhich mainly affects the lungs, although it can also cause allergies or affect other regions of the respiratory tract, causing sinusitis or ear infections, for example.
This fungus is found in the environment and can even be found indoors, in humid environments, such as wall corners or bathrooms. By invading the lungs through breathing, the Aspergillus fumigatus causes lesions, called fungal balls or aspergillomas, which can cause coughing, shortness of breath, bloody phlegm, weight loss and fever.
How to deal with: Treatment for aspergillosis is with potent antifungals, such as Itraconazole or Amphotericin B, which should be used according to the doctor’s instructions. Understand how aspergillosis is treated.
6. Paracoccidioidomycosis
Also called South American blastomycosis, this infection is caused by fungi from the family Paracoccidioideswhich inhabits the soil and plants, which is why this infection is more common in rural areas.
Transmission occurs mainly through the air, when the fungus is inhaled, which penetrates the lungs and bloodstream, causing symptoms such as lack of appetite, weight loss, cough, shortness of breath, fever, itching, skin wounds and the appearance of rashes. Learn how to identify the symptoms of paracoccidioidomycosis.
How to deal with: Treatment for this infection is generally long, lasting from months to years, and the use of antifungals, such as Itraconazole, Fluconazole, Ketoconazole or Voriconazole, for example, is normally recommended. In the most serious cases, where the lung does not perform its function correctly or the fungus has reached other organs, treatment must be carried out in the hospital.
7. Histoplasmosis
It is an infection caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatumwhich is transmitted through inhalation of fungi present in nature.
The disease usually develops in people with weakened immunity, such as immunological diseases, AIDS or malnutrition, for example, or people who inhale a large amount of fungi. Signs and symptoms that may occur are cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, fever and weight loss.
How to deal with: When the person is healthy, the infection with this fungus can disappear without any specific treatment. However, in more serious cases, especially when the immune system is compromised, the doctor may recommend the use of systemic antifungals, such as Itraconazole, Ketoconazole or Amphotericin B, for example, preventing the fungus from reaching the bloodstream and reaching other organs, resulting in serious complications.
8. Mucormycose
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus disease, is an infection caused by the fungus Rhizopus spp., which can be found naturally in vegetation, soil, fruits and decomposition products.
Transmission of this disease occurs through inhalation of spores of the fungus, which leads to the appearance of symptoms such as headache, nasal and eye discharge, redness of the face, cough with phlegm, fever and, in the most serious cases, convulsions and loss of consciousness.
How to deal with: Treatment is carried out through the injection of antimycotic medications intravenously or use of the medication orally, such as Amphotericin B or Posaconazole, according to the doctor’s instructions. Furthermore, if tissue necrosis is found, surgery may also be indicated to remove the parts affected by the fungus. Learn more about mucormycosis.
9. Cryptococcosis
Popularly known as pigeon disease, cryptococcosis is a disease caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformanswhich can be transmitted through inhalation of spores of this fungus that can be found in pigeon feces and in fruits, cereals, trees and soil.
After inhalation, the spores lodge in the lungs, resulting in respiratory symptoms such as coughing, nasal discharge, chest pain and the development of lung nodules. However, if the immune system is weakened, more serious symptoms may be noticed, such as weakness, stiff neck, fever, mental confusion, headache, meningitis and visual changes, and it is important that treatment is carried out immediately.
How to deal with: The treatment of cryptococcosis must be guided by the doctor and varies according to the severity of the disease. Therefore, antifungal medications, such as Amphotericin B or Fluconazole, may be indicated for 6 to 10 weeks.
In cases where it is possible to detect the fungus in the blood, hospitalization is necessary to prevent possible complications that could put the person’s life at risk.
10. Blastomicose
Blastomycosis is an infection caused by the fungus Blastomyces dermatitidiswhich can be found in moist soils, decaying wood and in places where there is vegetation.
This disease occurs through inhalation of fungal spores, resulting in symptoms such as cough, fever, phlegm, chest pain, shortness of breath, joint pain, weight loss and, in the most serious cases, the development of pneumonia. Furthermore, the fungus can spread through the bloodstream and affect other organs such as skin, bones, joints and brain, with the infection being more serious in people with a weaker immune system.
How to deal with: The treatment indicated by the doctor depends on the symptoms presented by the person and the state of the person’s immune system and includes the use of antimycotics, such as Itraconazole, in solution or tablet, or Amphotericin B intravenously for 6 to 12 months.
How to prevent diseases caused by fungi
Fungi are infectious agents naturally present in the environment and in the body, as is the case with Candida sp., for example, without causing any symptoms of disease, since the immune system can easily combat it. However, fungal disease is more common in people who have a weakened immune system, due to age or chronic illnesses.
Thus, one of the ways to prevent fungal infections is to increase immunity, and it is interesting to consume foods rich in vitamin C, A and E, omega-3, zinc and probiotics, in addition to practicing physical activity regularly and drinking at least 2 liters of water per day. Check out other tips to improve immunity.
Furthermore, in cases where the infection is related to the manipulation of soil, vegetation or animals that may carry the fungus, it is important to use a mask and protective glasses, as this makes it possible to avoid contact with the fungus spores. , preventing infection.
It is also interesting to avoid making the environment too humid, as this environment is favorable to the development of fungi. In the case of genital candidiasis, for example, it is important to keep the genital region always clean and dry and avoid wearing very tight clothing, as this can promote air circulation, preventing the area from becoming too humid and causing the proliferation of the virus. fungus.

Sign up for our newsletter and stay up to date with exclusive news
that can transform your routine!
Warning: Undefined array key "title" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 12
Warning: Undefined array key "title_tag" in /home/storelat/public_html/wp-content/plugins/link-whisper-premium/templates/frontend/related-posts.php on line 13